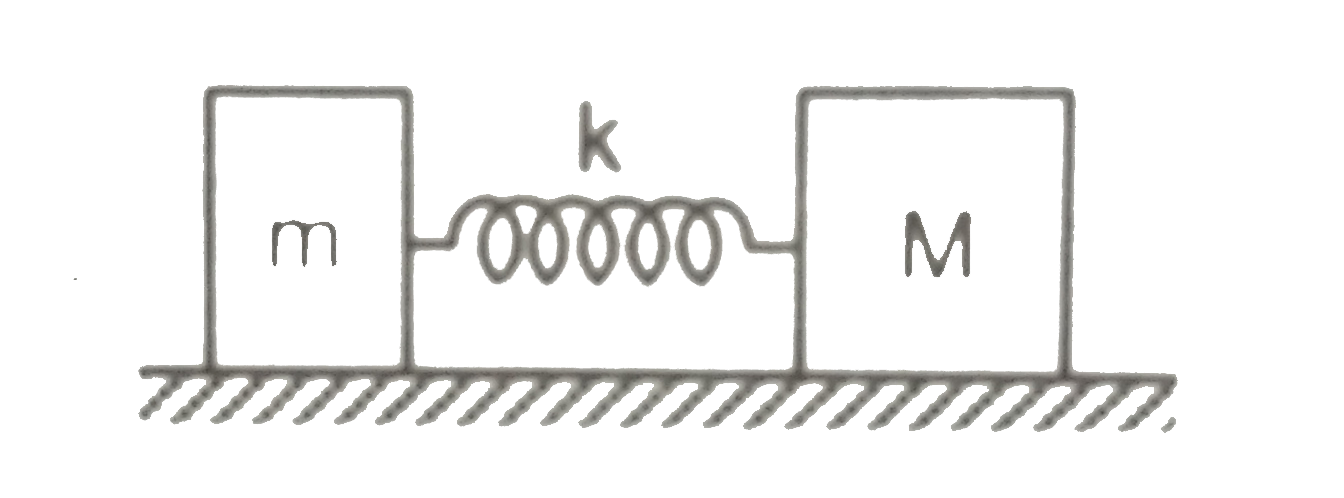
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-MECHANICS-EXERCISE
- A sphere is moving with velocity vector 2hati+2hatj immediately before...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles having position vectors vec(r )(1) = ( 3 hat(i) + 5 hat(...
Text Solution
|
- A light spring of spring constant k is kept compressed between two blo...
Text Solution
|
- Force acting on a particle is )jˆ3 iˆ (2 N. Work done by this force ...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum of mass 1 kg and length = 1m is released from rest at ang...
Text Solution
|
- The system is released from rest with both the springs in unstretched ...
Text Solution
|
- In previous question maximum speed of the block placed horizontally is...
Text Solution
|
- A particle undergoes uniform circular motion. About which point on the...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal circular plate is rotating about a vertical axis passing...
Text Solution
|
- A disc is rolling without slipping with angular velocity omega. P and ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform thin rod of mass m and length L is standing vertically along...
Text Solution
|
- A spinning ballet dancer changes the shape of her body by spreading he...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass M object of mass M is attached to the rim and r...
Text Solution
|
- A spool with a thread wound on it is placed on a smooth inclined plane...
Text Solution
|
- A bar of mass M and length L is in pure traslatory motion with its of ...
Text Solution
|
- A small particle of mass m is given an initial high velocity in the ho...
Text Solution
|
- A long horizontal rod has a bead which can slide along its length and ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Two balls of different masses are thrown vertically upward ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: For projection angle tan^(-1)(4), the horizontal range and ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A coin is placed on phonogram turn table. The motor is sta...
Text Solution
|