Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-TEST PAPERS-Physics
- A true balance is one whose pans are of equal masses and arms are of e...
Text Solution
|
- A lamina is made by removing a small disc of diameter 2 R from a bigge...
Text Solution
|
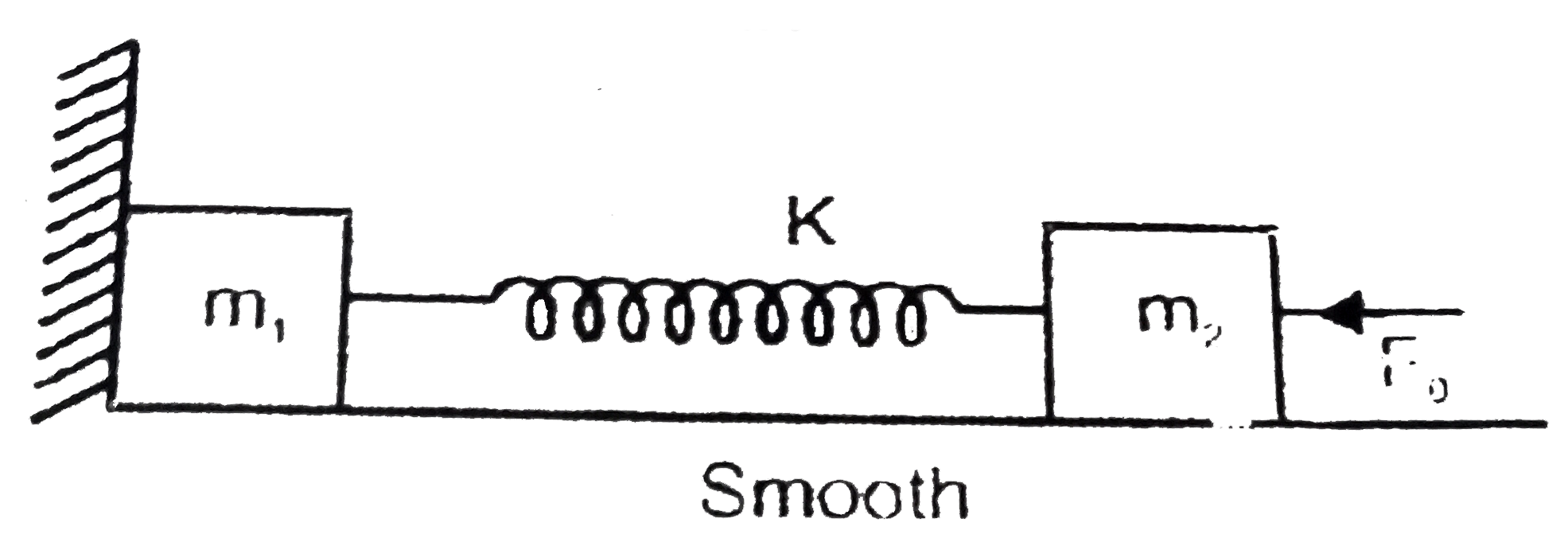
- Given system is in equilibrium. All surfaces are smooth. Spring is ide...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform solid sphere of mass M and radius R is rotating with respect...
Text Solution
|
- 32 capacitor are connected in a circuit as shown in the figure. The ca...
Text Solution
|
- Maximum power transfer to external circuit in watt will be
Text Solution
|
- A tunnel is dug inside the earth across one of its diameters. Radius o...
Text Solution
|
- An object kept on the principle axis is moving in the sme directions a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle performs simple harmonic motion with amplitude A. its speed...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform string of length 10 m is suspended from a rigid support A sh...
Text Solution
|
- A travelling wave travelled in string in +x direction with 2 cm//s, pa...
Text Solution
|
- A person throws a ball in vertical plane such that velocity of ball al...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of masses m and 2 m has initial velocity vecu(1)=2hati+3...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R is released gentiy on a horizont...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C is charged to a potential ...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball thrown at an initial velocity v(0) at an angle alpha to t...
Text Solution
|
- A dipole of dipole moment vecp=phati is kep at the centre of a circle ...
Text Solution
|
- In each of three figure shown, two blocks are connected by a light spr...
Text Solution
|
- A ladder AB is spported by a smooth vertical wall ad rough horizontal ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of mass M and radius R is resting on two corner edges A and...
Text Solution
|