A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-MASTER PRACTICE PROBLEM-Additional topic
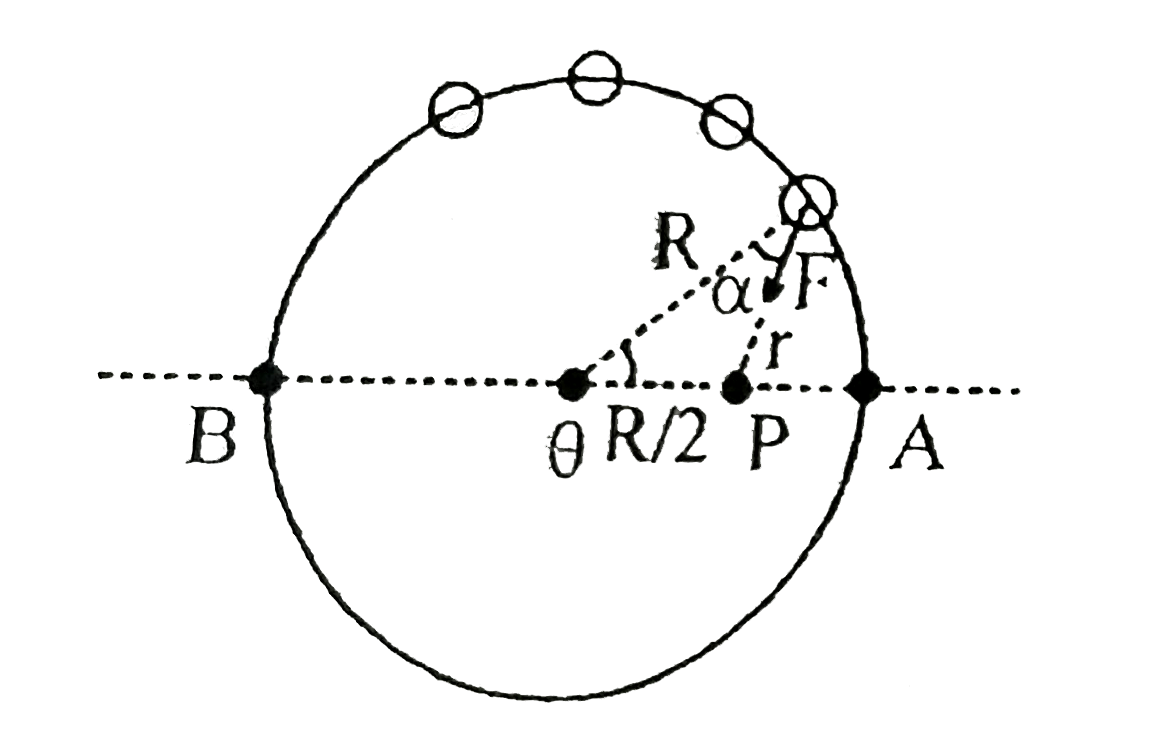
- A small bead of mass m can moves on a smooth circular wire (radiusR) u...
Text Solution
|
- The manifestation of band structure in solids is due to
Text Solution
|
- When p-n junction diode is forward biased then
Text Solution
|
- If the ratio of the concentration of electron to that of holes in a se...
Text Solution
|
- If the lattice constant of this semiconductor is decreased, then which...
Text Solution
|
- In the following, which one of the diodes is reverse biased ?
Text Solution
|
- The circuit has two oppositively connected ideal diodes in parallel wh...
Text Solution
|
- If a p-n junction diode, a square input signal of 10 V is applied as s...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit below, A and B represents two inputs and C represents t...
Text Solution
|
- A p-n junction (D) shown in the figure can act as a rectifier. An alte...
Text Solution
|
- The logic circuit shown below has the input waveforms ‘A’ and ‘B’ as s...
Text Solution
|
- The combination of gates shown below yields .
Text Solution
|
- Truth table for system of four NAND gates as shown in figure is : .
Text Solution
|
- In semiconductor the concentrations of electron and holes are 8xx10^(1...
Text Solution
|
- A potential difference of 2V is applied between the opposite faces of ...
Text Solution
|
- The main cause of avalence breakdown is
Text Solution
|
- A cube of germanium is placed between the poles of a magnet and a volt...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, which of the diodes are forward biased?
Text Solution
|
- Current in the circuit will be
Text Solution
|
- The diode used in the circuit shown in the figure has a constant volta...
Text Solution
|
- In the following circuits PN-junction diodes D(1), D(2) and D(3) are i...
Text Solution
|