A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SURFACE TENSION
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise- 3 PART - II|7 VideosSURFACE TENSION
RESONANCE|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|18 VideosSURFACE TENSION
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise- 2 PART - IV|5 VideosSTRING WAVES
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise|32 VideosUNITS, DIMENSION & MEASUREMENT
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-SURFACE TENSION-Exercise- 3 PART - I
- Water is filled up to a height h in a beaker of radiys R as shown in t...
Text Solution
|
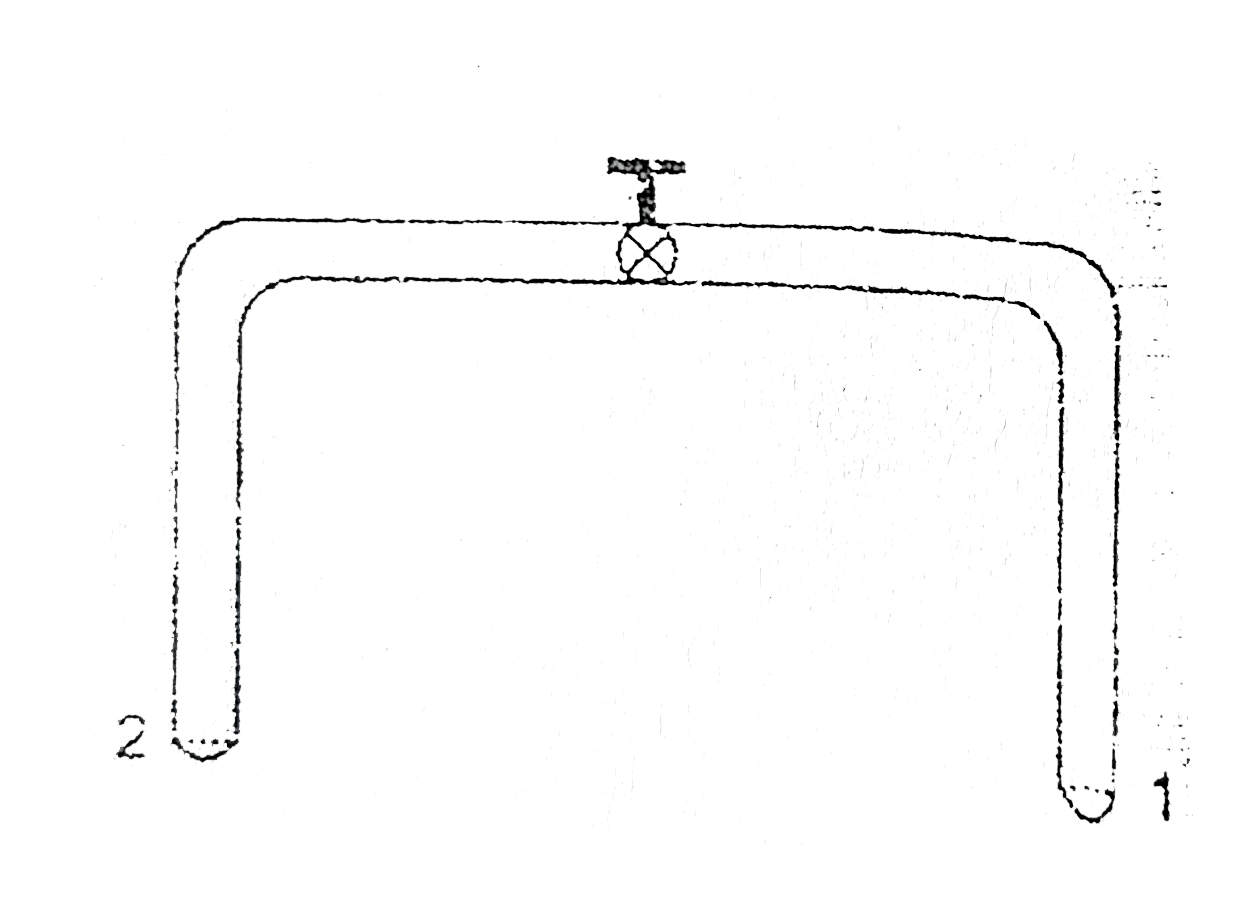
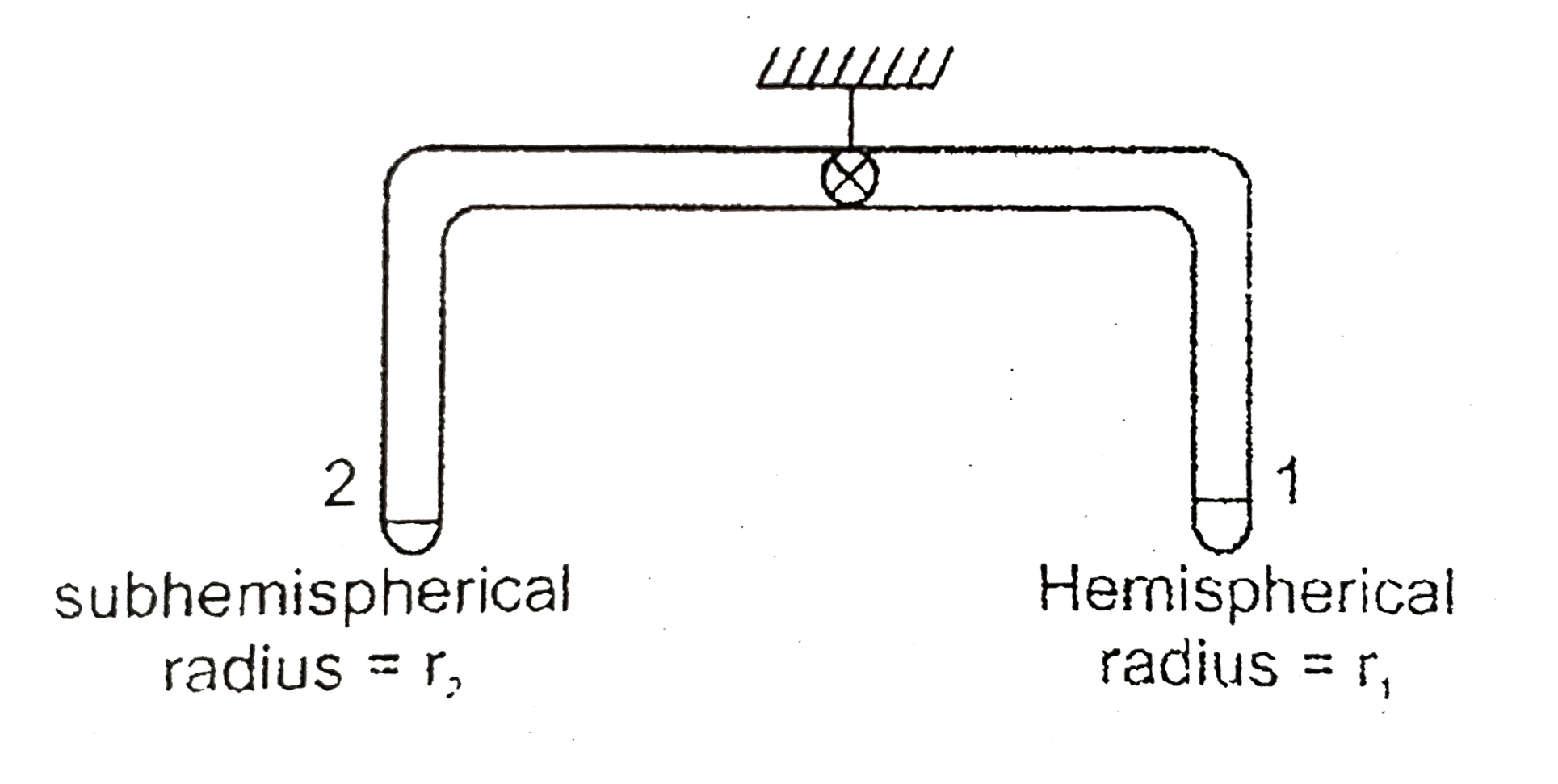
- A glass tube of uniform internal radius (r) has a valve separating the...
Text Solution
|
- Two soap bubbles A and B are kept in a closed chamber where the air is...
Text Solution
|
- When liquid medicine rho is to be put in the eye, it is done with the ...
Text Solution
|
- When liquid medicine of density rho is to be put in the eye, it is don...
Text Solution
|
- When liquid medicine of density rho is to be put in the eye, it is don...
Text Solution
|
- When liquid medicine rho is to be put in the eye, it is done with the ...
Text Solution
|
- When liquid medicine rho is to be put in the eye, it is done with the ...
Text Solution
|