Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-GRAVITATION-EXERCISE -4 Section - B
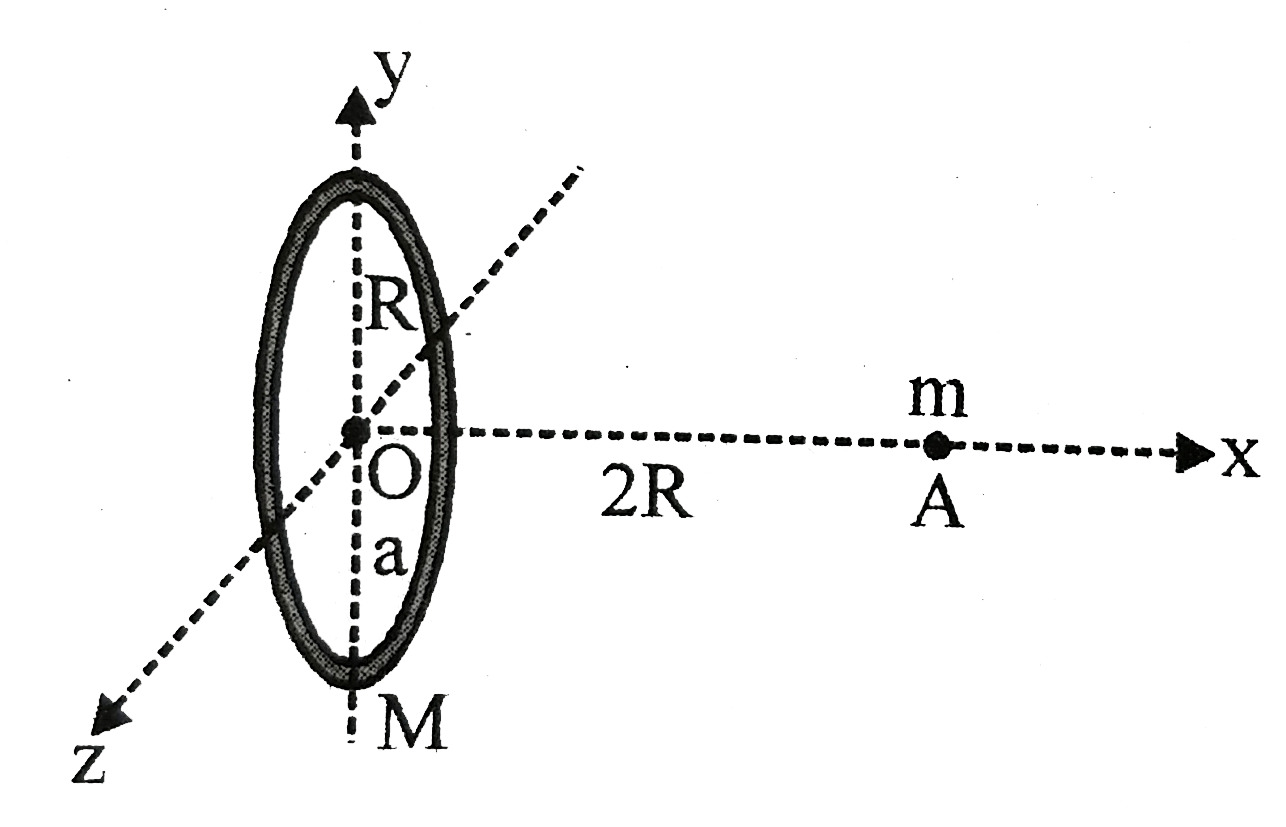
- A circular ring of mass M and radius R is placed in YZ plane with cent...
Text Solution
|
- A planet in a distant solar systyem is 10 times more massive than the ...
Text Solution
|
- The height at which the acceleration due to gravity becomes (g)/(9) (w...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of masses m and 4m are placed at a distance r. The gravitat...
Text Solution
|
- What is the minimum energy required to launch a satellite of mass m fr...
Text Solution
|
- Four particles, each of mass M and equidistant from each other, move a...
Text Solution
|
- From a solid sphere of mass M and radius R, a spherical portion of rad...
Text Solution
|