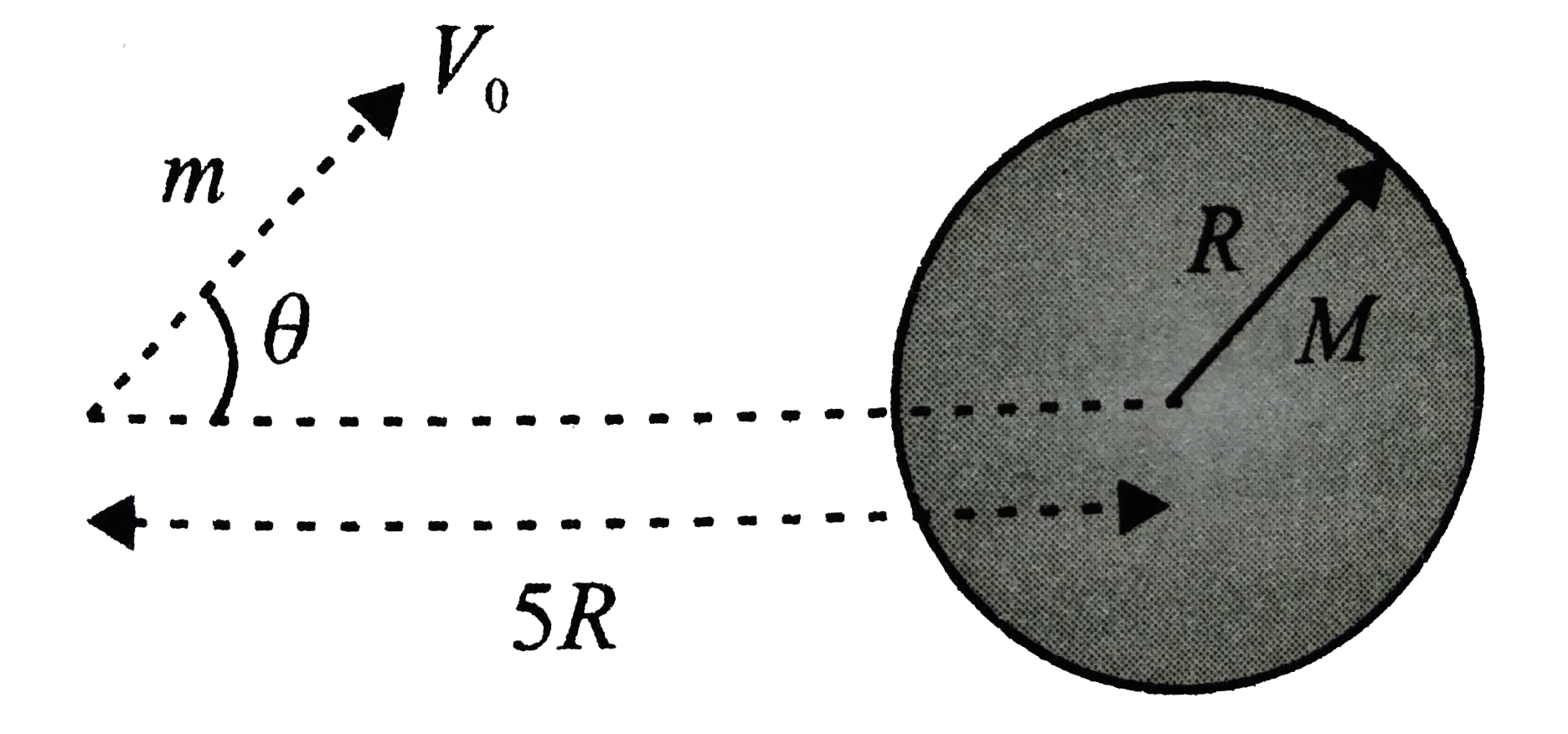
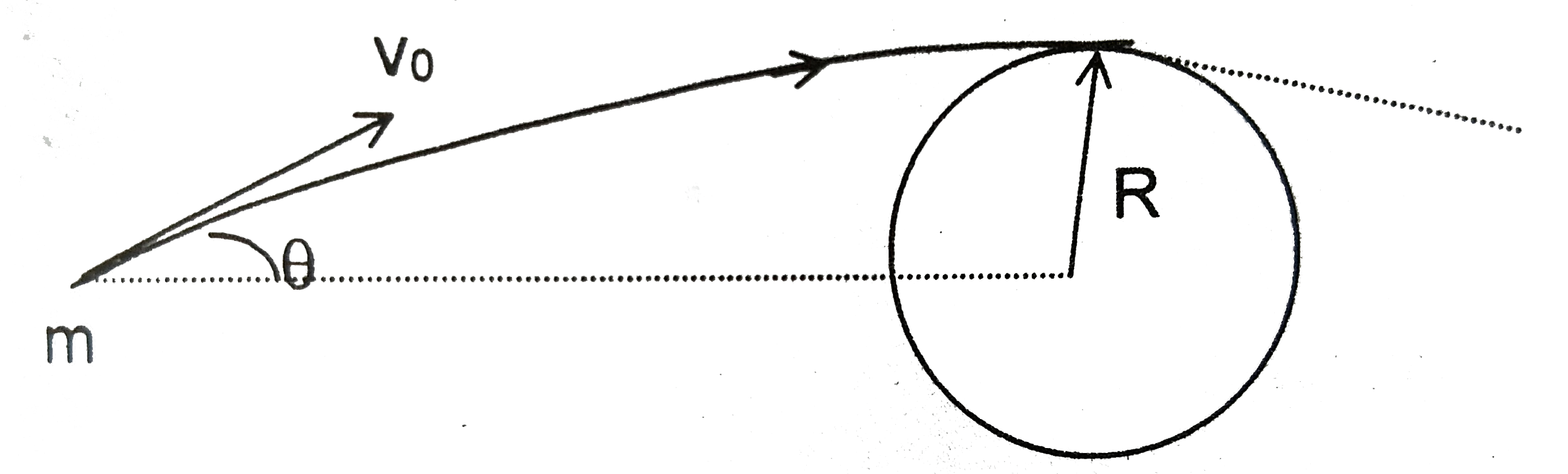
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GRAVITATION
BANSAL|Exercise Practice Exercise|18 VideosGRAVITATION
BANSAL|Exercise EXERCISE -1 [Single Correct Choice Type]|21 VideosGRAVITATION
BANSAL|Exercise EXERCISE -4 Section - B|6 VideosCENTRE OF MASS & MOMENTUM CONSERVATION
BANSAL|Exercise EXERCISE-4 (SECTION-B) (JEE-ADVANCED Previous Year Questions)|8 VideosHEAT TRANSFER
BANSAL|Exercise Exercise|89 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-GRAVITATION-Solved Example
- A satellite is revolving round the earth in a circular orbit of radius...
Text Solution
|
- If a satellite is revolving around a planet of mass M in an elliptical...
Text Solution
|
- A planet of mass m moves along an ellipse around the sun so that its m...
Text Solution
|
- A spaceship is sent to investigate a planet of mass M and radius R. Wh...
Text Solution
|
- A missile is launched at an angle of 60^(@) to the vertical with a vel...
Text Solution
|
- find the minimum coaltitude which can directly receive a signal from a...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite of mass M(S) is orbitting the earth in a circular orbit of...
Text Solution
|
- Two Earth's satallites move in a common plane along circular orbits. T...
Text Solution
|