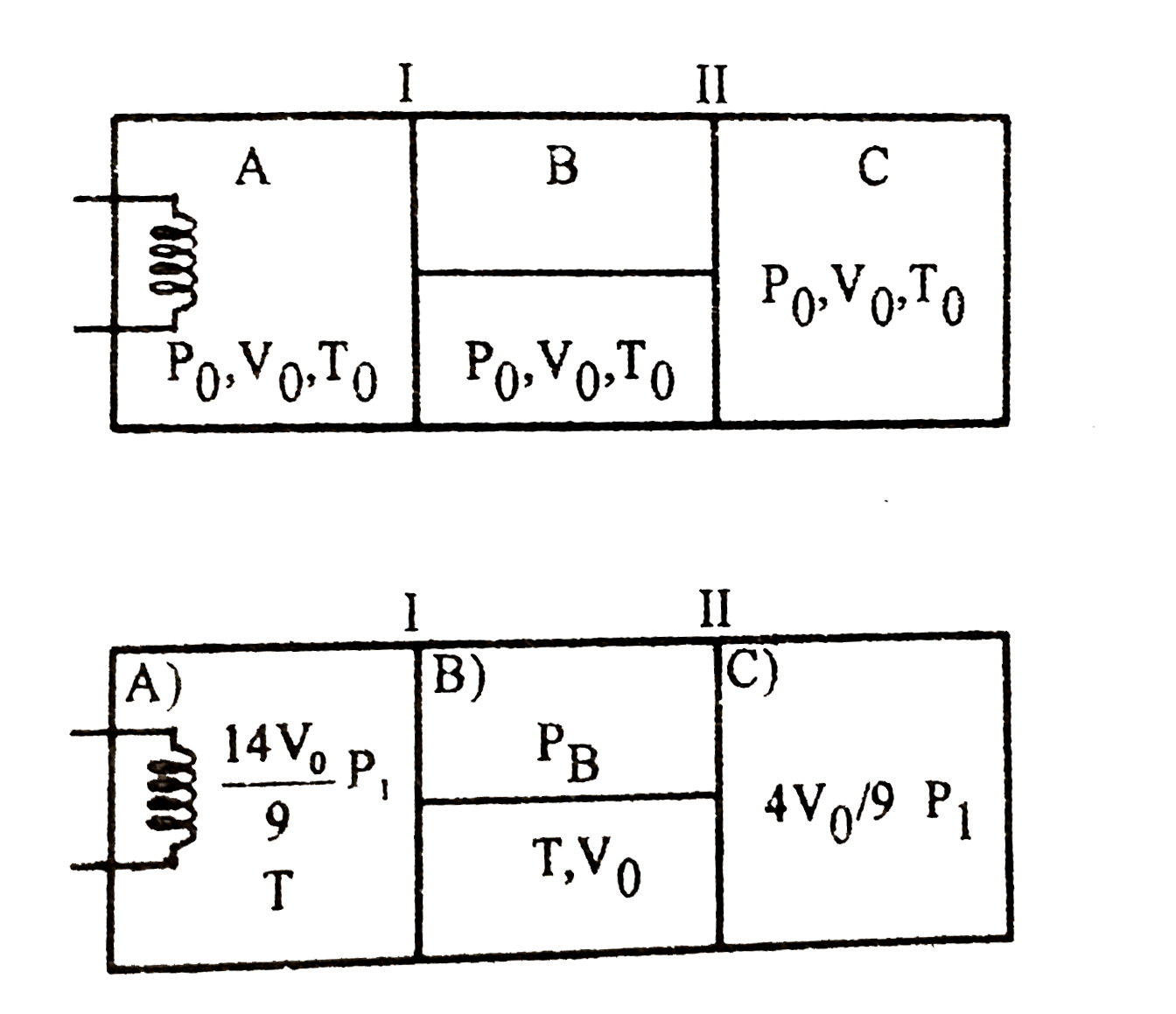A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BANSAL-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES-Exercise-3
- A motor car tyre is pumped up to pressure of two atmosheres at 15^(@)C...
Text Solution
|
- The volume of one mode of an ideal gas with adiabatic exponent gamma i...
Text Solution
|
- In a polytropic process an ideal gas (y= 1.40) was compressed from v...
Text Solution
|
- A volume of gas at atmospheric pressure is compressed adiabatically to...
Text Solution
|
- A gas at constant pressure P1, volume V1 and temperture T1 is suddenl...
Text Solution
|
- A mole of a monatimic perfect gas is adiabatically comporessed when it...
Text Solution
|
- In a certain polytropic process the volume of argon was increased alph...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas at a temperature T(1) expands according to th...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical hollow cylinder contains an ideal gas. The gas is enclosed ...
Text Solution
|
- The molar heat capacity of a perfect gas at constant volume is Cv. The...
Text Solution
|
- A 3000 - mL flask is initailly open while in a room containing air at ...
Text Solution
|
- A cyclic process for an ideal monatomic gas (Cv = 12.5 J mol^1 K^1)is ...
Text Solution
|
- A heat-conducting piston can freely move inside a closed thermally ins...
Text Solution
|
- Three moles of an ideal gas (Cp=7/2R) at pressure, PA and temperature ...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of a certain gas at a temperature T0=300K were cooled isocho...
Text Solution
|
- A certain volume of dry air at 20^(@)C is expanded to three thimes its...
Text Solution
|
- A certain volume of a gas (diatomic) expands isothermally at 20^(@)C u...
Text Solution
|
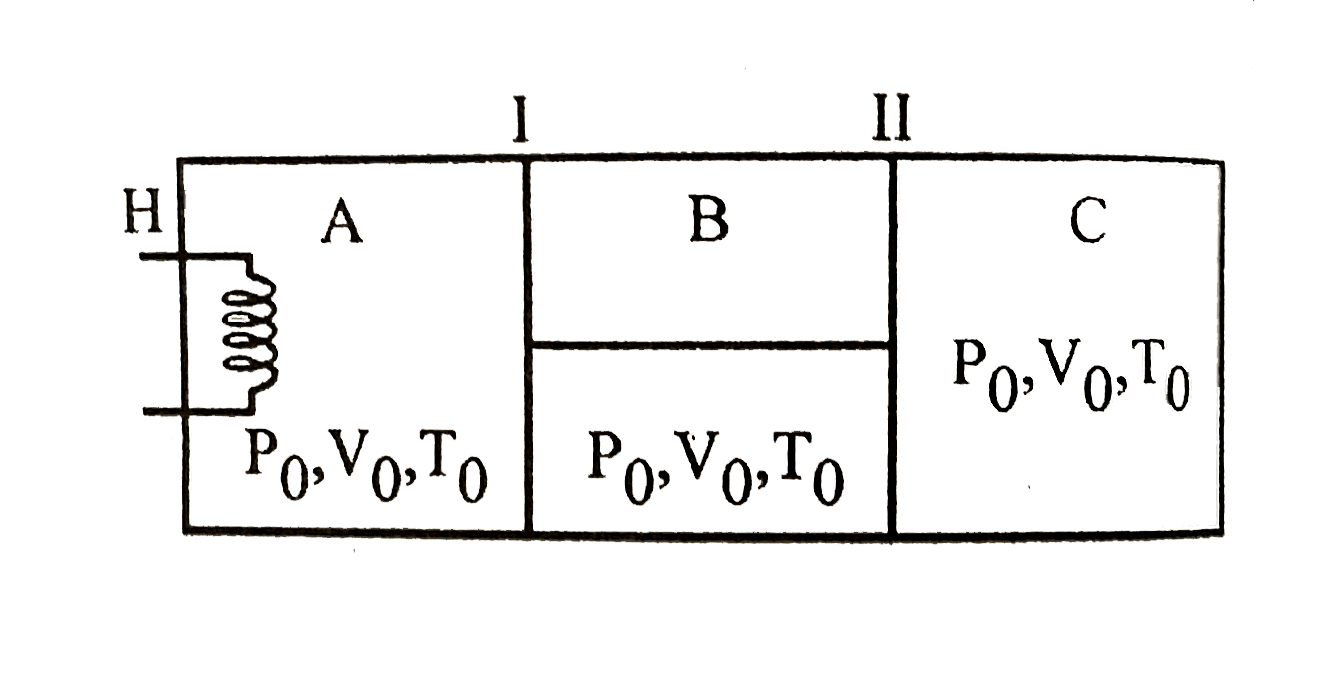
- The figure shows an insulated cylinder divided into three parts A,B a...
Text Solution
|
- A thermally insulated vessel is divided in to two parts by a heat insu...
Text Solution
|
- A gas takes part in two processes in which it is heated from the same ...
Text Solution
|