Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ANURAG MISHRA-RIGID BODY MOTION-MATCH THE COLUMN
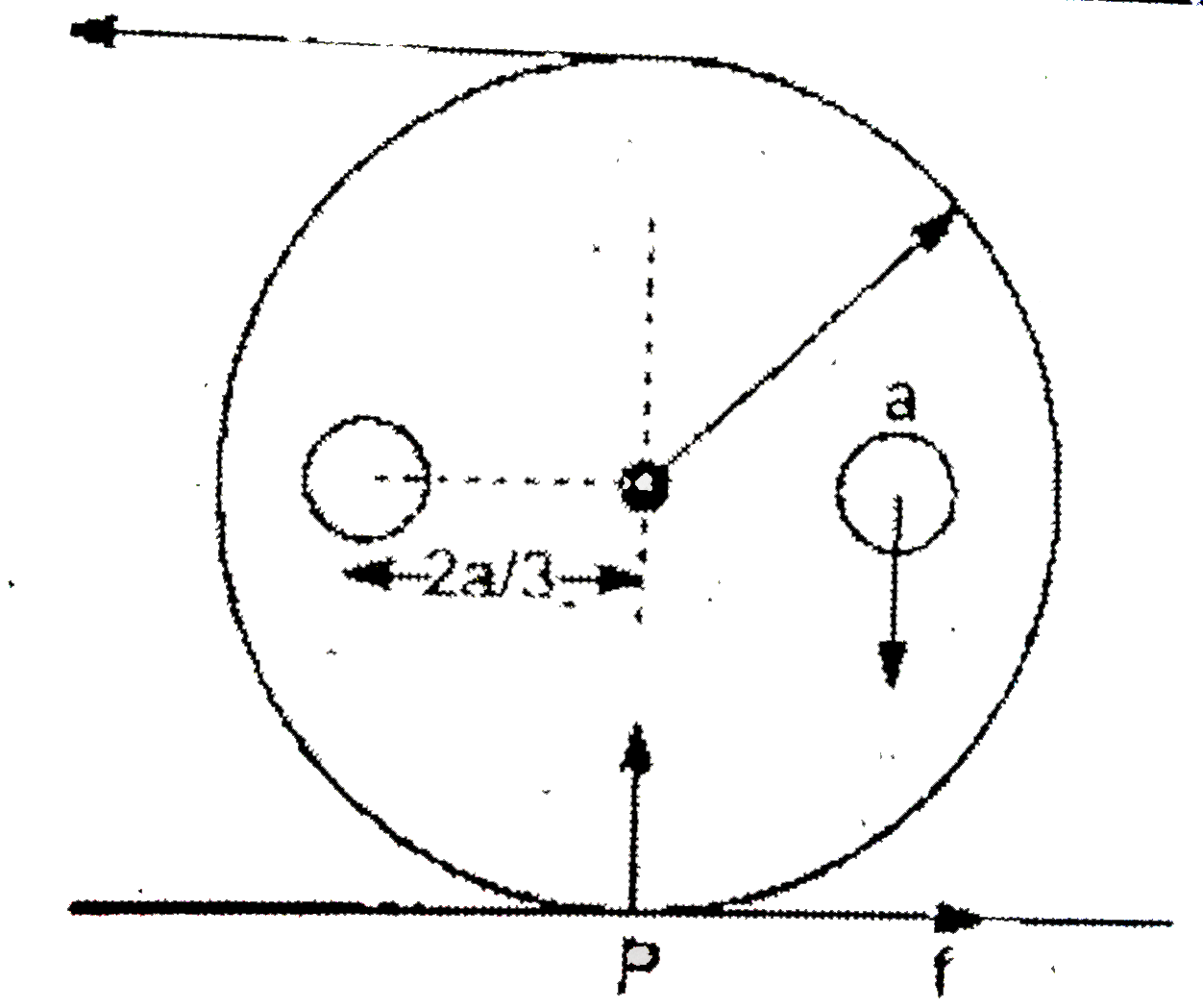
- Fig shows a uniform cylinder of radius a weight 75N. After on off axis...
Text Solution
|
- Match the statements, situations in Column I with that in Column II. O...
Text Solution
|
- Match the statements, situations in Column I with that in Column II. O...
Text Solution
|
- Match the statements, situations in Column I with that in Column II. O...
Text Solution
|
- Match the statements, situations in Column I with that in Column II. O...
Text Solution
|
- For different bodies of circular cross-section of same mass and radius...
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
- In column various bodies of same mass and radius R are being lowered o...
Text Solution
|
- All the rigid bodies lie in smooth horizontal plane.
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
- Each object shown in column I has mass 2m. The ring has mass m and rad...
Text Solution
|
- A spol is lying on a rough horizontal surface. Forces F(1),F(2),F(3) a...
Text Solution
|
- Column I shows a rigid body of circlar cross-section projected on a ro...
Text Solution
|