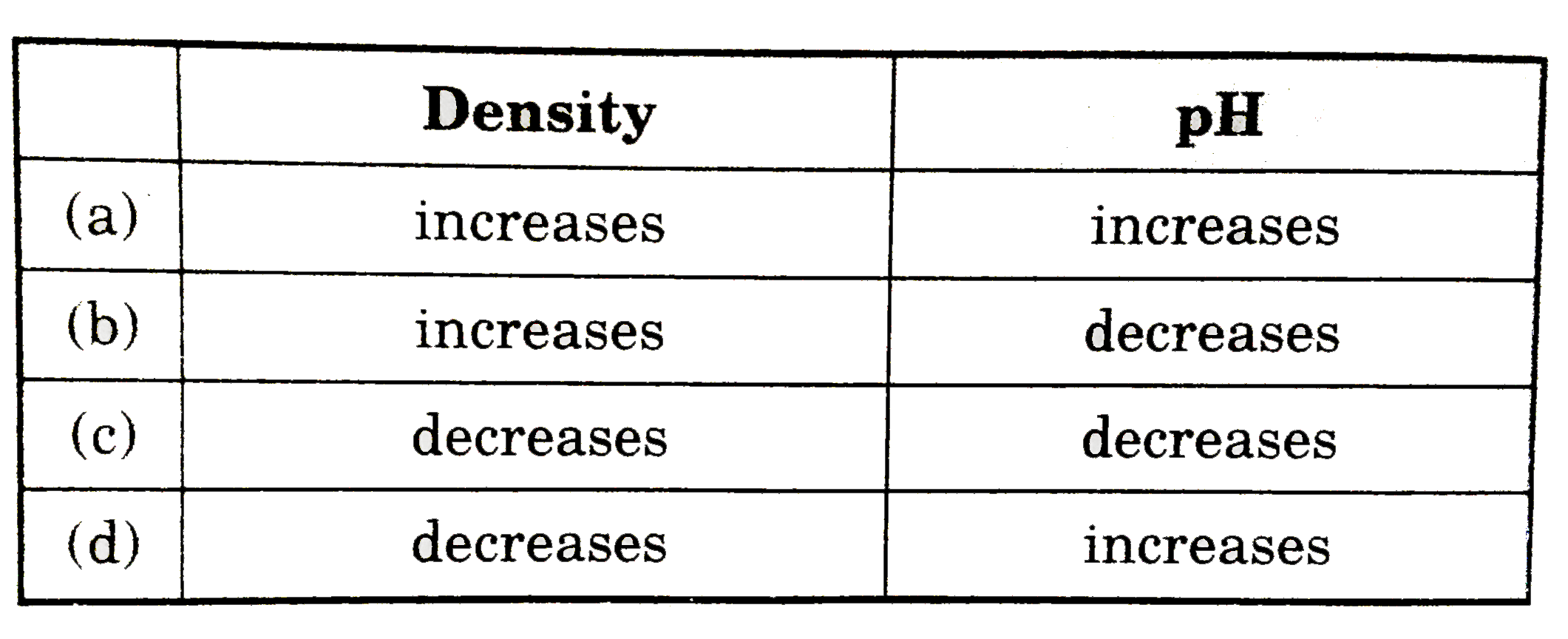
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROCHEMISTY
GRB PUBLICATION|Exercise Thermodynamics in Electrochemistry|22 VideosELECTROCHEMISTY
GRB PUBLICATION|Exercise Faraday s Laws and Electrolysis|87 VideosELECTROCHEMISTY
GRB PUBLICATION|Exercise Latimer Diagram, concentration cells|117 VideosD-BLOCK ELEMENTS
GRB PUBLICATION|Exercise Subjective Type|18 VideosENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
GRB PUBLICATION|Exercise Straight objective type|40 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
GRB PUBLICATION-ELECTROCHEMISTY-Batteries
- The overall reaction for the lead storage batter when it discharges is...
Text Solution
|
- The advantage of methane fuel cells over internal combusion engines (I...
Text Solution
|
- Rechargable batteries include which of the those below? (P) Dry cell...
Text Solution
|
- During discharge of a lead storage cell the density of sulphuric acid ...
Text Solution
|
- In H(2)-O(2) fuel cell the reaction occurring at cathode is:
Text Solution
|
- In a H(2) rightarrow O(2) fuel cell, 6.81 L of hydrogen at STP reacts ...
Text Solution
|
- While charging the lead storage battery:
Text Solution
|
- Equivalent weight of H(2)SO(4) in the following reaction (Pb(s) + PbO(...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the processes happen during the discharging of a lead storage...
Text Solution
|
- The equation for one of the half-reactions in a lead storage battery i...
Text Solution
|