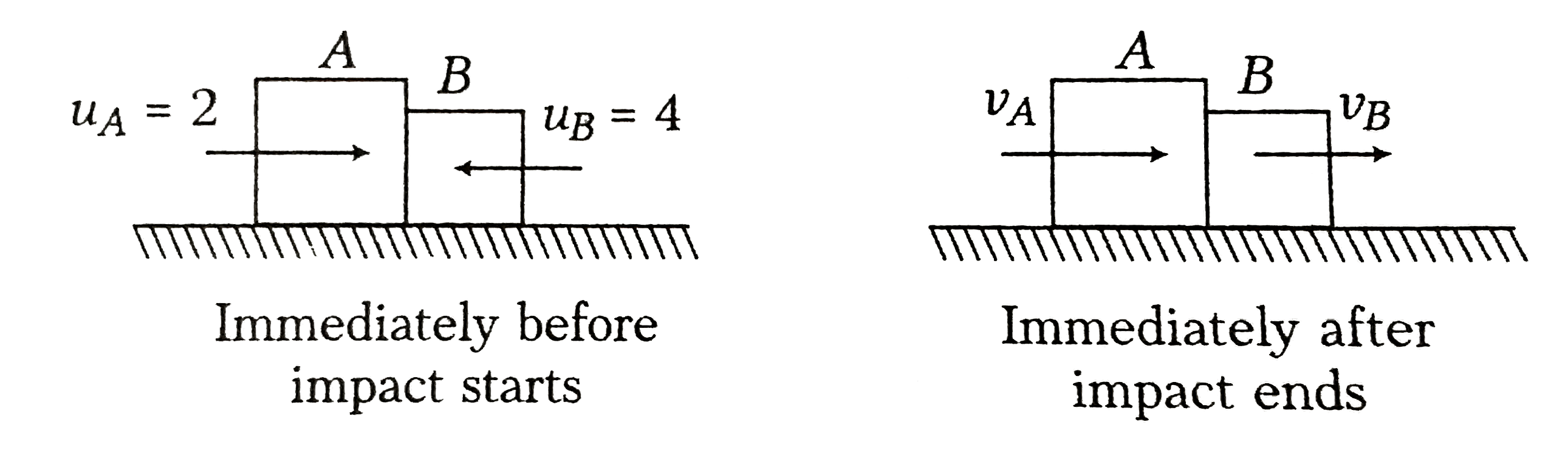Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-CENTRE OF MASS-Medical entrances gallery
- A block of mass 5 kg moves from left to right with a velocity of 2ms^(...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of weight w is supported by two parallel knife edges A and B an...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of masses m(1),m(2) move with initial velocities u(1) an...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a smooth curved track terminating in a smooth horizon...
Text Solution
|
- A block having mass m collides with an another stationary block having...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth curved surface of height 10 m is ended horizontally. A spring...
Text Solution
|
- A frog sits on the end of a long board of length L = 5 m. The board re...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m, collides with another stationary particle of mas...
Text Solution
|
- A body from height h is dropped, if the coefficient of restitution is ...
Text Solution
|
- Three particles of masses 0.50 kg, 1.0 kg and are placed at the corner...
Text Solution
|
- A large number of particles are placed around the origin, each at a di...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc rolls on a horizontal floor without slipping and the c...
Text Solution
|
- The linear momentum of a particle varies with time t as p= a +bt + ct^...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass (4m) is laying in xy-plane at rest. It suddenly explode...
Text Solution
|
- The position of center of mass of a system of particles does not depen...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet is fired from the gun. The gun recoils, the kinetic energy of...
Text Solution
|
- An explosion blows a rock into three parts. Two parts go off at right ...
Text Solution
|
- The linear momentum is conserved in
Text Solution
|
- Three particles , each of mass m, are placed at the vertices of a righ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 'm' moving with a horizontal velocity 'v' strikes the b...
Text Solution
|
- In an inelastic collision
Text Solution
|