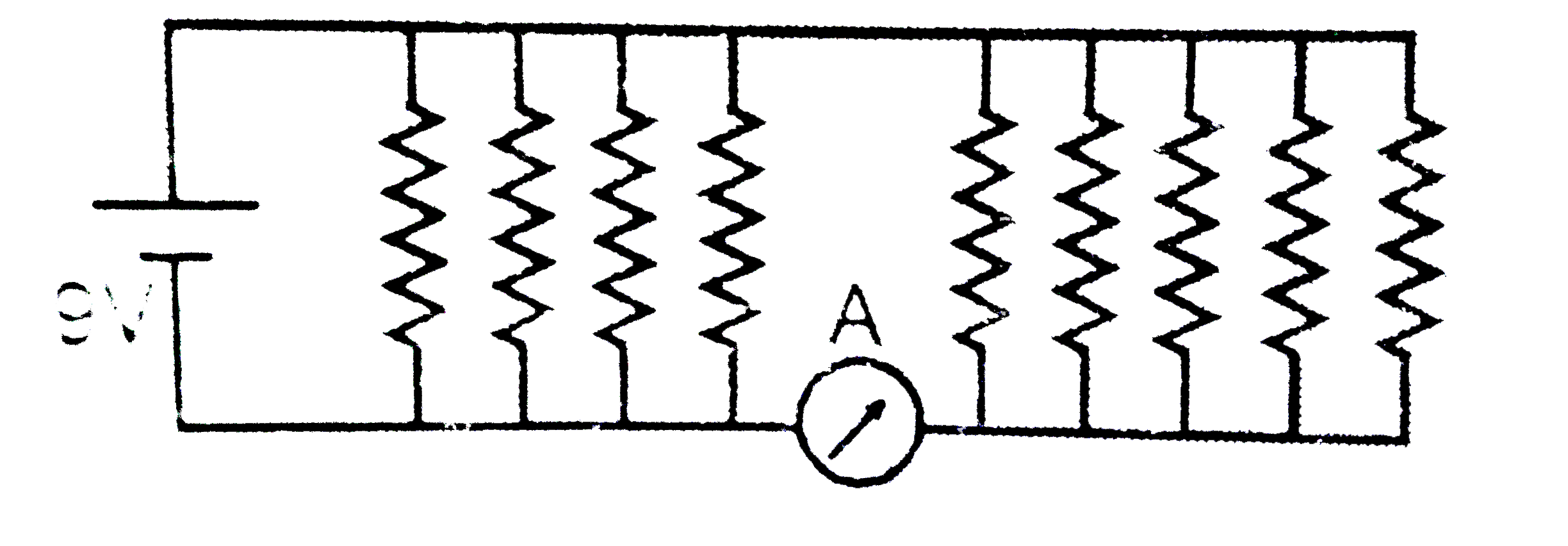
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-CENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM-Comprehension type questions
- Comprehension # 1 If net force on a system in a particular direction...
Text Solution
|
- Comprehension # 1 If net force on a system in a particular direction...
Text Solution
|
- Comprehension # 1 If net force on a system in a particular direction...
Text Solution
|
- Comprehension # 1 If net force on a system in a particular direction...
Text Solution
|
- Comprehension # 2 When two bodies collide normally they exert equal ...
Text Solution
|
- Comprehension # 2 When two bodies collide normally they exert equal ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identiacal masses are as shown in figure. One is thrown upwards wi...
Text Solution
|
- Two identiacal masses are as shown in figure. One is thrown upwards wi...
Text Solution
|
- Two identiacal masses are as shown in figure. One is thrown upwards wi...
Text Solution
|
- Comprehension # 4 When the mass of a system is variable, a thrust fo...
Text Solution
|
- Comprehension # 4 When the mass of a system is variable, a thrust fo...
Text Solution
|
- Comprehension # 4 When the mass of a system is variable, a thrust fo...
Text Solution
|
- Acceleration of two identical particles moving in a straight line are ...
Text Solution
|
- Acceleration of two identical particles moving in a straight line are ...
Text Solution
|
- Comprehension # 5 One particle of mass 1 kg is moving along positive...
Text Solution
|