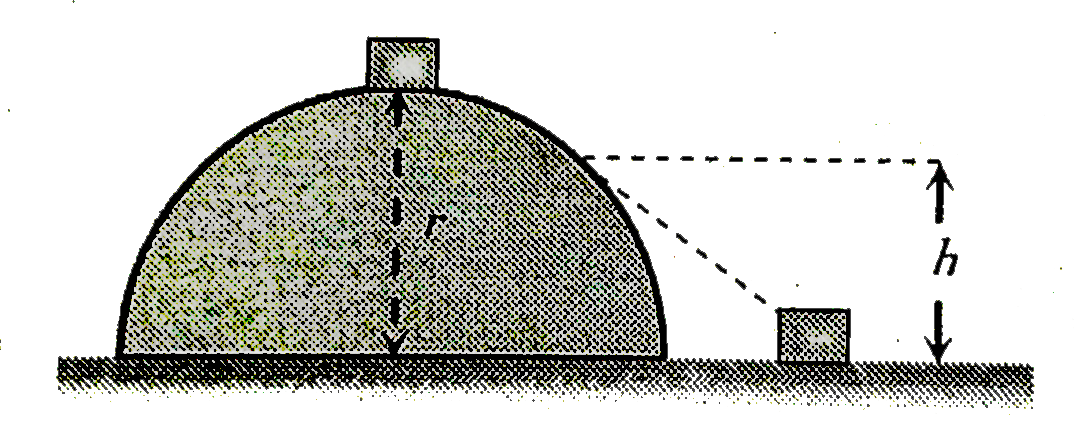
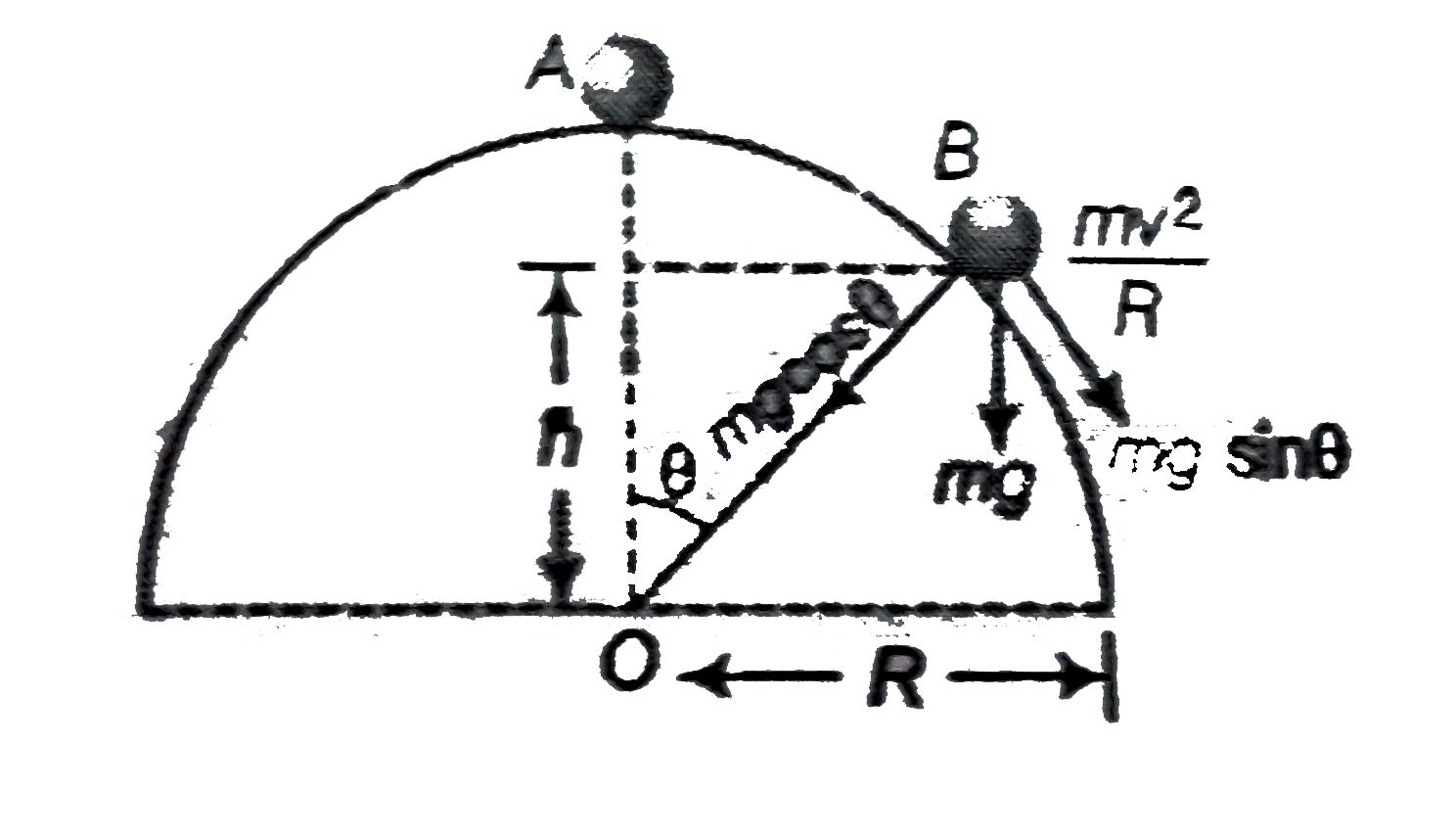
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BITSAT GUIDE-CIRCULAR MOTION-BITAST Archives
- A small body of mass m slides down from the top of a hemisphere of rad...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m= 20 g is attached to an elastic spring of length L=50...
Text Solution
|
- A car is moving on a circular road of diameter 50 m with a speed of 5...
Text Solution
|
- An inclined track ends in a circular loop of radius r. From what heigh...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball descibes a horozontal circle on the smooth inner surface ...
Text Solution
|
- The angle turned by a body undergoing circular motion depends on time ...
Text Solution
|