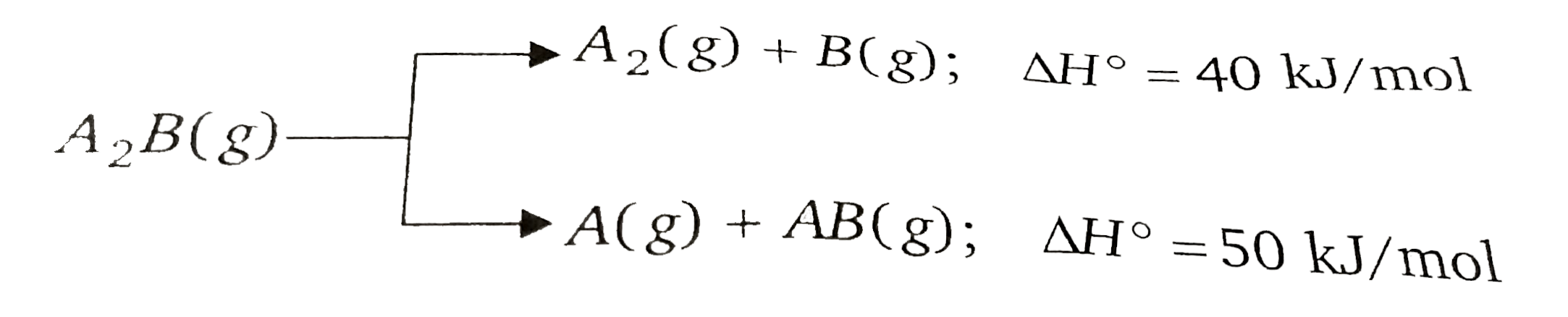A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-THERMODYNAMICS-Level -V
- At 25^(@)C, when 1 mole of MgSO(4) was dissolved in water, the heat ev...
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpy of neutraliztion of weak base A OH and a strong base BOH ...
Text Solution
|
- Substance A(2)B(g) can undergoes decomposition to form two set of prod...
Text Solution
|
- What is the bond enthalpy of Xe-F bond if Ionization energy of Xe = 27...
Text Solution
|
- In conversion of lime-stone to lime, CaCO(3(s)) to CaO((s)) + CO(2(g...
Text Solution
|
- 1 mole of an ideal gas A(C(v.m)=3R) and 2 mole of an ideal gas B are...
Text Solution
|
- When 1.0 g of oxalic acid (H(2)C(2)O(4)) is burnt in a bomb calorimete...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas is carried through the reversible cyclic proc...
Text Solution
|
- A gas (C(v.m) = (5)/(2)R) behaving ideally is allowed to expand revers...
Text Solution
|
- For polytropic process PV^(n) = constant, molar heat capacity (C(m)) o...
Text Solution
|
- 2 mole of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes a reversible process for w...
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpy of neutralization of a Weak monoprotic acid (HA) in 1 M s...
Text Solution
|
- If enthaopy of hydrogenation of C(6)H(6)(l) into C(6)H(12)(l) is -205k...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate DeltaS for 3 mole of a diatomic ideal gas which is heated an...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas at 27^(@)C is subjected to a rever...
Text Solution
|
- For a perfectly crystalline solid C(p,m)=aT^(3)+bT, where a and b are ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate Delta(r)G^(@) for (NH(4)Cl,s) at 310K. Given :Delta(r)H^(@...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate Delta(f)H^(@) (in kJ/mol) for Cr(2)O(3) from the Delta(r)G^(...
Text Solution
|
- The value of DeltaH("transition") of C (graphite) rarr C (diamond) is ...
Text Solution
|
- Select the correct statements:
Text Solution
|