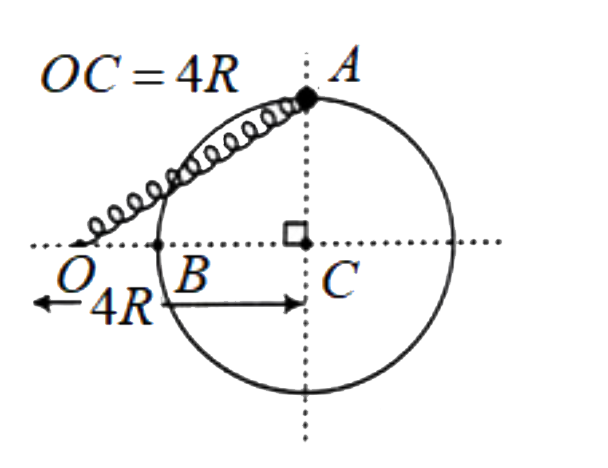
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NTA MOCK TESTS-JEE MOCK TEST 21-PHYSICS
- A 10 muF capacitor is charged to a potential difference of 50 V and is...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 2 xx 10^-5 kg moves horizontally between two horizo...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical vessels contain two different ideal gases at the same te...
Text Solution
|
- The K(alpha) line obtained for molybdenum (Z = 42) is 0.71 Å. Then, th...
Text Solution
|
- Wire having tension 225 N produces six beats per second when it is tun...
Text Solution
|
- The arrangement is released from rest. The minimum angle theta at whic...
Text Solution
|
- The length and breadth of a metal sheet are 3.124m and 3.002m respecti...
Text Solution
|
- A bead of mass m can slide without friction on a fixed circular horizo...
Text Solution
|
- There is a thin uniform disc of radius R and mass per unit area σ in w...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of mass M and radius R lies on a plank of mass M as shown. ...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires of the same material (Young's modulus=Y) and same length L b...
Text Solution
|
- A layer of oil with density 724 kg m^(-3) floats on water of density 1...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform ball of radius r rolls without slipping down from the top of...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel contains two non-reactive gases neon (monoatomic) and oxygen ...
Text Solution
|
- In a transistor, the collector current varies by 0.49 mA and emitter c...
Text Solution
|
- If in nuclear fission, a piece of uranium of mass 6.0 g is lost, the e...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit, what is the current (in A) through the battery?
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer coil has a resistance 90 Omega and full scale deflectio...
Text Solution
|
- At what distance from a convex mirror of focal length 2.5 m should a b...
Text Solution
|
- The resistance of each straight section r = 2 Omega. Find the equivale...
Text Solution
|