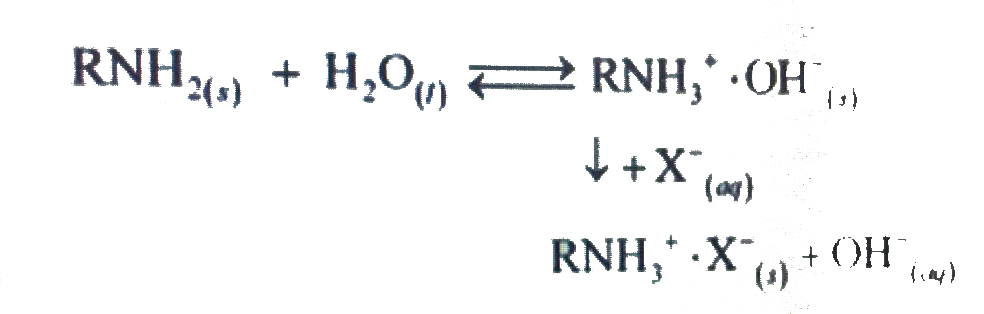Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT-HYDROGEN-EXERCISE
- Compare the stuctures of H(2)O and H(2)O(2).
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by the term 'auto-protolysis' of water? What is...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the reacton of water with F(2) and suggest, in terms of oxida...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following chemical reactions. (i) PbS(s)+H(2)O(2)(aq) t...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the structure of the common form of ice.
Text Solution
|
- What causes the temporary and permanent hardness of water ?
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the principle and method of softening of hard water by synthet...
Text Solution
|
- Write chemical reactions to show the amphoteric nature of water.
Text Solution
|
- Write chemical reactions to justifty that hydrogen peroxide can functi...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by 'demineralised water' and how it can be obtained?
Text Solution
|
- Is demineralised or distilled water useful for drinking purpose? If no...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the usefulness of water in bioshphere and biological systems.
Text Solution
|
- What properties of water make it useful as a solvent? What types of co...
Text Solution
|
- Knowing the properties of H(2)O and D(2)O, do you think that D(2)O can...
Text Solution
|
- What is the difference between hydrolysis and hydration?
Text Solution
|
- How can saline hydrides remove traces of water from organic compouds?
Text Solution
|
- What do you expect the nature of hydrides is, it formed by elements of...
Text Solution
|
- Do you expect different products in solution when aluminium (III) chlo...
Text Solution
|
- How does H(2)O(2) behave as a bleaching agent?
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by the terms: (i) hydrogen economy (ii) hydroge...
Text Solution
|