(a)
The O.N. (oxidation number) of P decreases from 0 in `P_(4)` to` –3` in `PH_(3)` and increases from 0 in `P_(4)` to + 2 in `HPO_(2)^(-)`. Hence, `P_(4)` acts both as an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent in this reaction.
Ion-electron method : The oxidation half reaction is :
`Prs to HPO2 `- (aq)
The P atom is balanced as :
P4 s `to` 4 HPO2- (aq)
The H atom is balanced by adding 12 `H^(+)` ions :
`P4s + 8 H2O to 4 HPO2 `- (aq) + 12 H+
The charge is balanced by adding `e^(-)` as
P4s + 8H2O `to` 4HPO2 - (aq) + 12 H+ + `8e^(-)`.... (i)
The reaction half equation is :
`P_(4 (s)) to PH_(3 (g))`
The P atom is balanced as
P4(s) `to` 4 PH3(g)
The H is balanced by adding `12 H^(+)` as :
P4 (s) + 12`H + to 4 PH3(g)`
The charge is balanced by adding `12 e^(-)` as :
`P4(s) + 12 H + + 12 e- to 4 PH3(g) .... ii`
By multiplying equation (i) with 3 and (ii) with 2 and then adding them, the balanced chemical equation can be obtained as:
`5P4(s) + 24H2O to 12 HPO2 - +8 PH3(g) + 12 H+`
As , the medium is basic add `12 OH^(-)` both sides as :
`5P4(s) + 12 H2O + 12 OH- to 12 HPO2 to +8PH3(g)`
This is the required balanced equation.
Oxidation number method : Let , total no of P reduced = x
`therefore`
Total no of P oxidised = `4 -x `
`P4 (s) + OH - to x PH3(g) + 4 - x HPO2 -`
(i) Total decrease in oxidation number of P = ` x xx 3 = 3 x`
Total increase in oxidation number of P = `(4 -x) xx 2 = 8- 2x `
`therefore `
`3 x = 8 - 2 x x = 8//5 `From (i)
`5P4(s) + 5 OH- to 8 PH3(g) + 12 HPO2 - `
Since , reaction occures in basic medium , the charge is balanced by adding `7OH^(-)` on LHS as :
5P4(s) + 12 OH- `to` 8PH3(g) + 12 HPO2 -
The O atoms are balanced by adding `12 H_(2)O` as :
5P4(s) + 12 H2O + 12 OH - `to `+ 12 HPO2 - + 8PH3(g)
This is the required balanced equation .
(b)
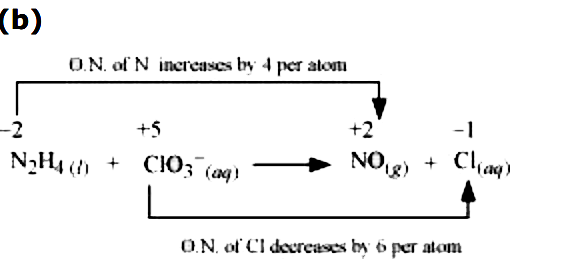
The oxidation number of N increases from `-2` in `N_(2)H_(4)` to +2 in NO and the oxidation number of Cl decreases from +5 in `ClO_(3)^(-)` to -1 in `Cl^(-)` Hence , in this reaction , `N_(2)H_(4)` is the reducing agent and `ClO_(3)^(-)` to -1 in `Cl^(-)` . Hence , in this reaction `N_(2)H_(4)` is the reduction agent and `ClO_(3)^(-)` is the oxidizing agent .
Ion - electron method :
The oxidation half equation is :
`overset(-2)(N_(2))H_(4(l)) to overset(+2)(N)O_((g))`
The N atoms are balanced as :
`N_(2)H_(4(l)) to 2 NO_((g)) + 8 e^(-)`
The charge is balanced by adding `8 OH^(-)` as .
`N_(2)H_(4 (l)) + 8 OH_((aq))^(-) to 2 NO_((aq)) + 8 e^(-)`
The O atoms are balanced by adding `6H_(2)O` as :
`N_(2)H_(4 (l)) + 8OH_((aq))^(-) to 2NO_((g)) + 6 H_(2) O_((l)) + 8 e^(-) ...... (i)`
The reduction half equation is :
`overset(+5)(C)lO_(3 (aq))^(-) to overset(-1)(C)l_((aq))^(-)`
The oxidation number is balanced by addition 6 electrons as :
`ClO_(3 (aq))^(-) + 6 e^(-) to Cl_((aq))^(-)`
The charge is balanced by adding `6OH^(-)` ions as :
`ClO_(3 (aq))^(-) + 6 e^(-) to Cl_((aq))^(-) + 6 OH_((aq))^(-)`
The O atoms are balanced by adding `3H_(2)O` as :
`Cl_(3 (aq))^(-) + 3H_(2)O_((l)) + 6e^(-) to Cl_((aq))^(-) + 6 OH_((aq))^(-) ......(ii)`
The balanced equation can be obtained by multiplying equation (i) with 3 and equation (ii) with 4 and then adding them as :
`3N_(2)H_(4 (l)) + 4 ClO_(3 (aq))^(-) to 6 NO_((g)) + 4 Cl_((aq))^(-) + 6 H_(2)O_((l))`
Oxidation number method :
Total decrease in oxidation number of N = `2 xx 4 = 8`
Total increase in oxidation number of Cl = `1 xx 6 = 6`
On multiplying `N_(2)H_(4)` with 3 and `ClO_(3)^(-)` with 4 to balance the increase and decrease in O.N. we get :
`3N_(2)H_(4 (l)) + 4 ClO_(3 (aq))^(-) to NO_((g)) + Cl_((aq))^(-)`
The N and Cl atoms are balanced as :
`3N_(2)H_(4 (l)) + 4 ClO_(3 (aq))^(-) to 6 NO_((g)) + 4 Cl_((aq))^(-)`
The O atoms are balanced by adding `6H_(2)O` as :
`3N_(2)H_(4 (l)) + 4 ClO_(3 (aq))^(-) + 6H_(2)O((l))`
This is the required balanced equation .
(c)

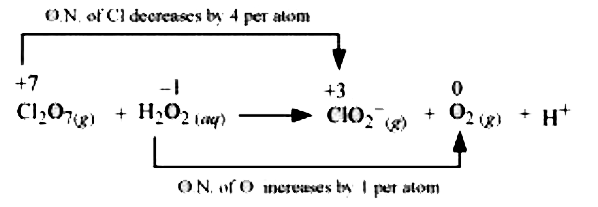
The oxidation number of Cl decreases from +7 in `Cl_(2)O_(7)` to +3 in `ClO_(2)^(-)` and the oxidation number of O increases from `-1` in `H_(2)O_(2)` to zero in `O_(2)` . Hence , in this reaction `Cl_(2)O_(7)` is the oxidizing agent and `H_(2)O_(2)` is the reducing agent .
Ion - electron method :
The oxidation half equation is :
`H_(2)overset(-1)(O)_(2(aq)) to overset(0)(O)_(2(g))`
The oxidation number is balanced by adding 2 electrons as :
`H_(2)O_(2 (aq)) to O_(2 (g)) + 2e^(-)`
The charge is balanced by adding `2OH^(-)` ions as :
`H_(2)O_(2 (aq)) + 2OH_((aq))^(-) to O_(2(g)) + 2 e^(-)`
The oxygen atoms are balanced by adding `2H_(2)O` as :
`H_(2)O_(2 (aq)) + 2 OH_((aq))^(-) to O_( 2(g)) + 2H_(2)O_((l)) + 2e^(-) " " (i)`
The reduction half equation is :
`overset(+7)(C)l_(2)O_(7 (g)) to overset(+3)(C)lO_(2 (aq))^(-)`
The Cl atoms are balanced as :
`Cl_(2)O_(7(g)) to 2 ClO_(2 (aq))^(-)`
The oxidation number is balanced by adding 8 electrons as :
`Cl_(2)O_(7(g)) + 8 e^(-) to 2ClO_(2 (aq))^(-)`
The charge is balanced by adding `6 OH^(-)` as :
`Cl_(2)O_(7 (g)) + 8 e^(-) to 2 ClO_(2 (aq))^(-) + 6 OH_((aq))^(-)`
The oxygen atoms are balanced by adding `3H_(2)O` as :
`Cl_(2)O_(7(g)) + 3H_(2)O_((l)) 8e^(-) to 2ClO_(2 (aq))^(-) + 6 OH_((aq))^(-) " " (ii)`
The balanced equation can be obtained by multiplying equation (i) with 4 and adding equation (ii) to it as `Cl_(2)O_(7 (g)) + 4H_(2) O_(2 (aq)) to 2 ClO_(2 (aq))^(-) + 4 O_(2 (g)) + 5 H_(2)O_((l))`
Oxidation number method :
Total decrease in oxidation number of `Cl_(2)O_(7) = 4 xx 2 = 8`
Total increase in oxidation number of `H_(2)O_(2) = 2 xx 1 = 2 `
By multiplying `H_(2)O_(2)` and `O_(2)` with 4 to balance the increase and decrease in the oxidation number , we get :
`Cl_(2)O_(7 (g)) + 4 H_(2)O_(2 (aq)) to ClO_(2 (aq))^(-) + 4 O_(2 (g))`
The Cl atoms are balanced as :
`Cl_(2)O_(7 (g)) + 4 H_(2)O_(2 (aq)) to 2 ClO_(2 (aq))^(-) + 4 O_(2 (g))`
The O atoms are balanced by adding `3H_(2)O` as :
`Cl_(2) O_(7 (g)) + 4 H_(2)O_(2 (aq)) to 2 ClO_(2 (aq))^(-) + 4 O_(2 (g)) + 3 H_(2)O_((l))`
The H atoms are balanced by adding `2OH^(-)` and `2H_(2)O` as :
`Cl_(2)O_(7 (g)) + 4 H_(2)O_(2 (aq)) to 2 ClO_(2 (aq))^(-) + 4O_(2(g)) + 5 H_(2)O_((l))`
This is the required balanced equation .


