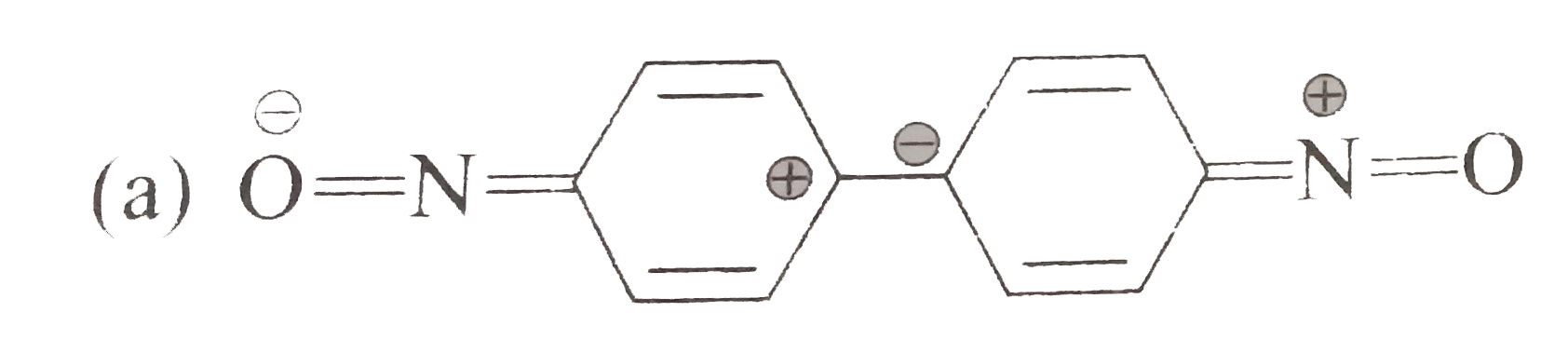
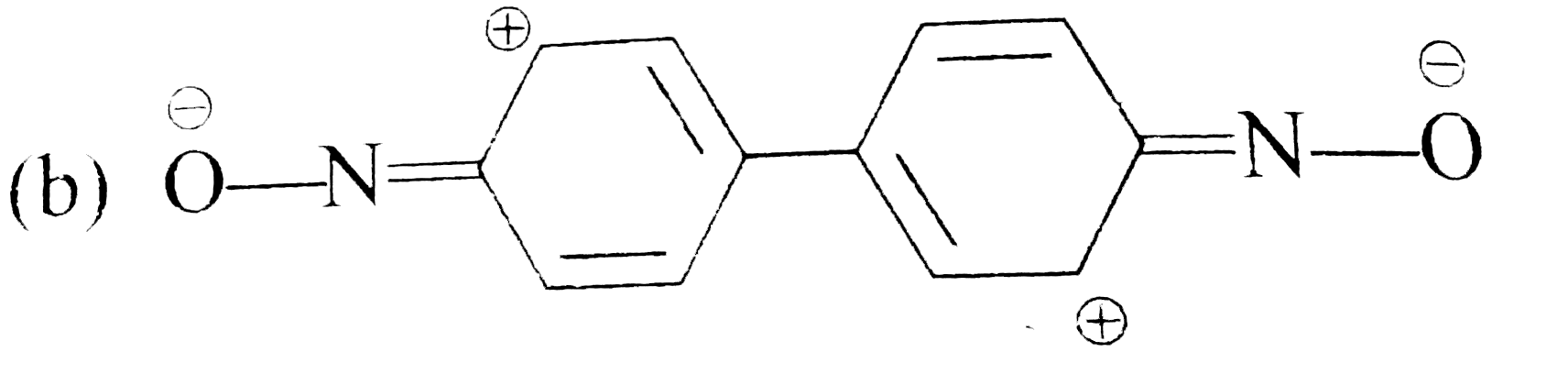
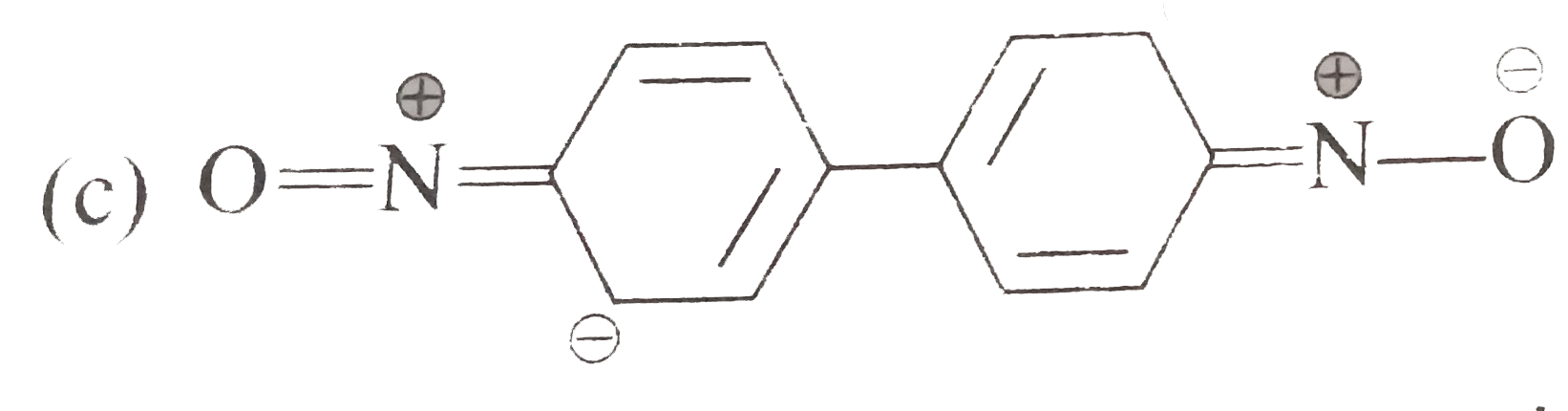
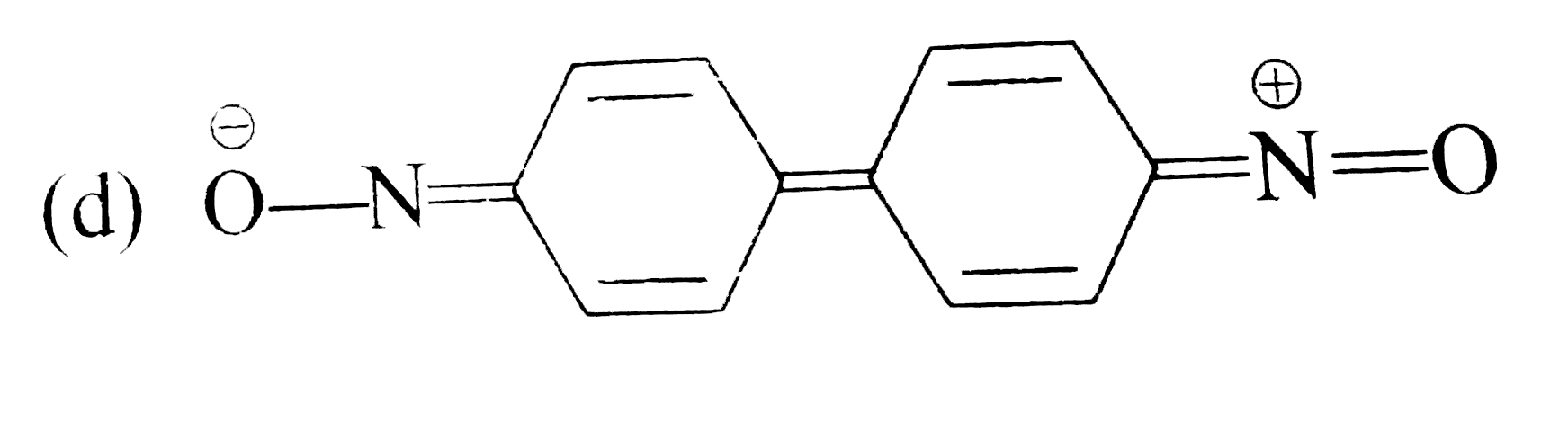
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Linked Comprehension Type (Q.26 To Q.27)|2 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Match The Column|9 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise More Than One Correct (Q.51 To Q.55)|5 VideosCHEMISTRY IN DAILY LIFE
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Integer Answer Type Problems|7 VideosHALIDES
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Subjective Type Problems|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HIMANSHU PANDEY-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-Linked Comprehension Type (Q.1 To Q.25)
- When (C-H)sigma electrons are in conjugation to pi bond this conjugati...
Text Solution
|
- In an aromatic ring, a functional group with lone pair of electron exe...
Text Solution
|
- In an aromatic ring, a functional group with lone pair of electron exe...
Text Solution
|
- In an aromatic ring, a functional group with lone pair of electron exe...
Text Solution
|
- The process whereby a hydrogen atom attached to the alpha-carbon of ca...
Text Solution
|
- The process whereby a hydrogen atom attached to the alpha-carbon of ca...
Text Solution
|
- The process whereby a hydrogen atom attached to the alpha-carbon of ca...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following cations rearrangement takes place?
Text Solution
|
- Under common reaction conditions, a carboncation rearranges to another...
Text Solution
|
- Under common reaction conditions, a carboncation rearranges to another...
Text Solution
|
- Type of anios in which delocatisation of negative charge occrur on mor...
Text Solution
|
- Type of anios in which delocatisation of negative charge occrur on mor...
Text Solution
|
- Type of anios in which delocatisation of negative charge occrur on mor...
Text Solution
|
- In a substance that are resonance hybirds, the measured length of give...
Text Solution
|
- In a substance that are resonance hybirds, the measured length of give...
Text Solution
|
- In a substance that are resonance hybirds, the measured length of give...
Text Solution
|
- Basicity is defined by equilibrium constant for abstracting a proton. ...
Text Solution
|
- Basicity is defined by equilibrium constant for abstracting a proton. ...
Text Solution
|
- Basicity is defined by equilibrium constant for abstracting a proton. ...
Text Solution
|
- Benzoic acid is more acidic than acetic acid, fomic acid is more acidi...
Text Solution
|
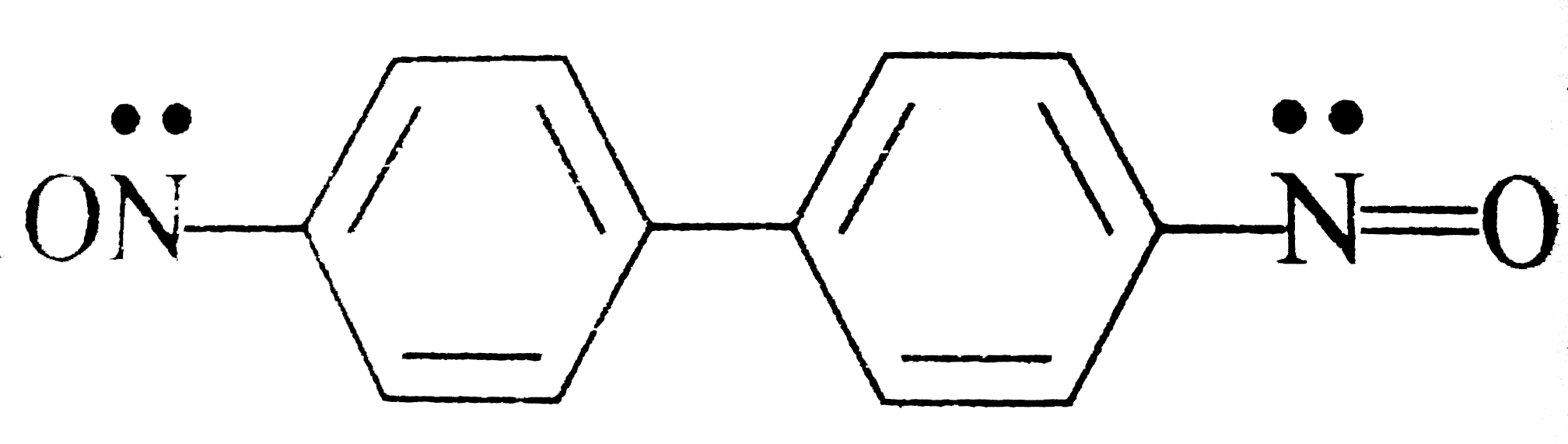 is
is