Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM-Exercise - 4
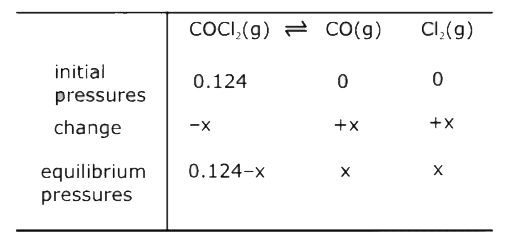
- Phosgene is a poisonous gas that dissociates at high temperature into ...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction, 2NO(2(g))hArr2NO((g)) + O(2(g)) K(c) = 1.0xx10^(-6) ...
Text Solution
|
- The exothermic formation of ClF(3) is represented by thr equation: C...
Text Solution
|
- A schematic plot of ln K(eq) versus inverse of temperature for a react...
Text Solution
|
- An amount of solid NH4HS is placed in a flask already containing ammon...
Text Solution
|
- Phosphorus pentachloride dissociates as follows, ina closed reaction v...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant for the given reaction: SO(3(g))hArrSO(2(g)...
Text Solution
|
- For the following three reaction 1, 2 and 3, equilibrium constants are...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant K(p(1)) and K(p(2)) for the reactions XhArr2Y...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel at 1000 K contains carbon dioxide with a pressure of 0.5 atm....
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant for the reaction N(2)(g)+O(2)(g) hArr 2NO(g...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction, SO(2)(g)+1/2O(2)(g)hArrSO(3)(g) if K(p)=K(C)(RT)^(x)...
Text Solution
|
- The standard Gibbs energy change at 300K for the reaction 2AhArrB+C is...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant at 298K for a reaction, A+BhArrC+D is 100. If...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following lines correctly show the temperature dependence...
Text Solution
|
- If Ag^(+)+NH(3)hArr[Ag(NH(3))]^(+), K(1)=3.5xx10^(-3) and [Ag(NH(3))]^...
Text Solution
|
- The thermal dissociation of equilibrium of CaCo(3)(s) is studied under...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction, SO(2)(g)+1/2O(2)(g)hArrSO(3)(g) if K(p)=K(C)(RT)^(x)...
Text Solution
|
- The % yield of ammonia as a function of time in the reaction N(2)(g) +...
Text Solution
|
- Thermal decomposition of gaseous X(2) to gaseous X at 298 K takes plac...
Text Solution
|
- Thermal decomposition of gaseous X(2) to gaseous X at 298 K takes plac...
Text Solution
|