Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM-Exercise - 3
- Consider the reaction of chloromethane with OH^(-) in aqueous solution...
Text Solution
|
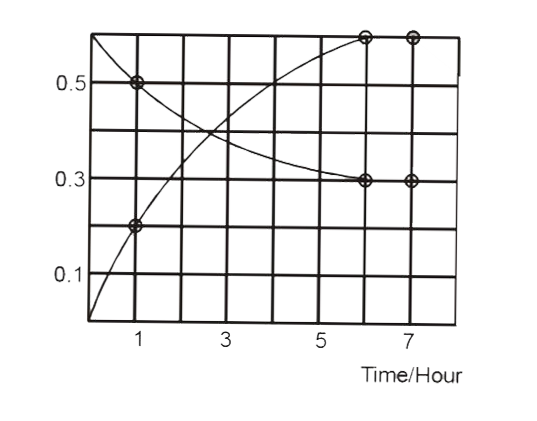
- The progress of the reaction AhArrnB with time, is presented in figure...
Text Solution
|
- The progress of the reaction AhArrnB with time, is presented in figure...
Text Solution
|
- The progress of the reaction AhArrnB with time, is presented in figure...
Text Solution
|
- If K(c) = 7.5 ×x 10^(-9) at 1000 k for the reaction N(2)(g) + O(2)(g)h...
Text Solution
|
- The degree of dissociation of N(2)O(4) into NO(2) at 1 atm 40^(@)C is ...
Text Solution
|
- At 46° C Kp for the reaction N(2)O(4) (g)hArr 2NO(2)(g) is 0.667 atm. ...
Text Solution
|
- At some temperature and under a pressure of 4 atm, PCl(5) is 10% disso...
Text Solution
|
- In a mixture of N(2) and H(2) in the ratio 1:3 at 30 atm and 300^(@)C,...
Text Solution
|
- The system N(2)O(4)hArr 2 NO(2) maintained in a closed vessel at 60° C...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour density of N(2)O(4) at a certain temperature is 30. Calcula...
Text Solution
|
- In the esterfication C(2)H(5)OH(1) + CH(3)COOH(1)hArrCH(3)COOC(2)H(5)(...
Text Solution
|
- 20.0 grams of CaCO(3)(s) were placed in a closed vessel, heated & main...
Text Solution
|
- An equilibrium mixture of PCl(5), PCl(3) and Cl(2) at a certain temper...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of HI (9.30 x× 10^(-3) mol) was placed in an empty 2.00 L con...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant for the reaction A((g))+2B((g)) rarr C((g)) i...
Text Solution
|
- The initial concentrations or pressure of reactants and products are g...
Text Solution
|
- The initial concentrations or pressure of reactants and products are g...
Text Solution
|
- The initial concentrations or pressure of reactants and products are g...
Text Solution
|
- The initial concentrations or pressure of reactants and products are g...
Text Solution
|