Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -3 (Level -II) SECTION E- Electrical Power & Energy|3 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -3 (Level -II) SECTION F- Electrical Instrument + Exp. Verifying ohm s law & Specific Resistance Using Meter Brige & post Office + Potentiometer (EMF & Int Res.)|3 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -3 (Level -II) SECTION B- Resistance & resistivity ,Ohms law +VI (Volt - Curr.) Characteristics + Colour Code + Temp . Dependence|6 VideosCONSTRAINED MOTION
MOTION|Exercise EXAMPLES|12 VideosELASTICITY
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -3|60 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-EXERCISE -3 (Level -II) SECTION C,D - Circuit theory , KCL & KVL , Battery , Grouping of cells
- A triangle is constructed using the wires AB, BC and CA of same materi...
Text Solution
|
- What will be the change in the resistance of a circuit consisting of f...
Text Solution
|
- A piece of resistive wire is made up into two squares with a common si...
Text Solution
|
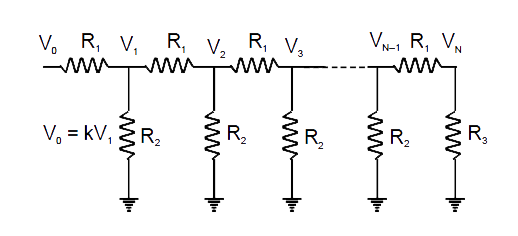
- A network of resistance is constructed with R(1)&R(2) as shown in the ...
Text Solution
|
- A network of resistance is constructed with R(1)&R(2) as shown in the ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in fig. calculate the following: a. Potential d...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in figure , calculate the following Current t...
Text Solution
|
- An equiring physics student connects a cell to a circuit and measures ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the potential difference V(A)-C(B) for the circuit shown in the ...
Text Solution
|