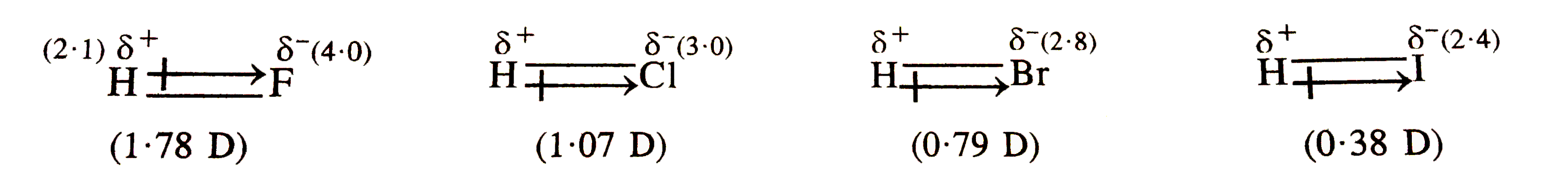Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise H.O.T.S. CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS|11 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise VALUE BASED QUESTIONS|2 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise BORD EXAMINATIONS|84 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit test|20 VideosCLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise All Questions|310 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DINESH PUBLICATION-CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE -ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT QUASTIONS
- What is the hybridisatio carbon atoms numbered as 1,2 and 4 in the fol...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by the term bond order ? Calculate the bond order ? Calc...
Text Solution
|
- The sdipole miment of hydrogen halides decreases form HF to HI. Explai...
Text Solution
|
- Which out of N(2) and H(2)O is polar and why ?
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the electronegativity value of chlorine on Mulliken's scale,...
Text Solution
|
- H(2)O molecule is a triatomic molecule but its geometry is not linear....
Text Solution
|
- (a) Which of the following species has greater polarising power ? (i...
Text Solution
|
- Why is lithium iodide more covalent than lithium fluoride ?
Text Solution
|
- Out of CS(2) and OCS which have higher dipole moment and why?
Text Solution
|
- Draw the Lewis structure of HCN.
Text Solution
|
- The presence of polar bonds in a polyatomic molecule suggests that the...
Text Solution
|
- Write two resonance structure of N2 O that satisfy the octet rule.
Text Solution
|
- Out of but-1-yne or but-1-ene which has higher dipole moment?
Text Solution
|
- Using VSEPR theory draw the shape of PCI(5) and BrF(5) ?.
Text Solution
|
- How does the bond length vary in dicarbon species C(2),C(2)^(-),C(2)...
Text Solution
|
- (a) How does bond energy vary from N(2)^(+) and N(2)^(-) and why ? ...
Text Solution
|
- Why is mobilty of H^(+) ions in ice greater as compared to liquid wate...
Text Solution
|
- According to Octed Rule, each atom gains or loses electrons to complet...
Text Solution
|
- L.C.A.O. principle is involved in the formation of molecular orbitals ...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange H(2)O,NH(3) and CH(4) molecules in decreasing order of bond an...
Text Solution
|