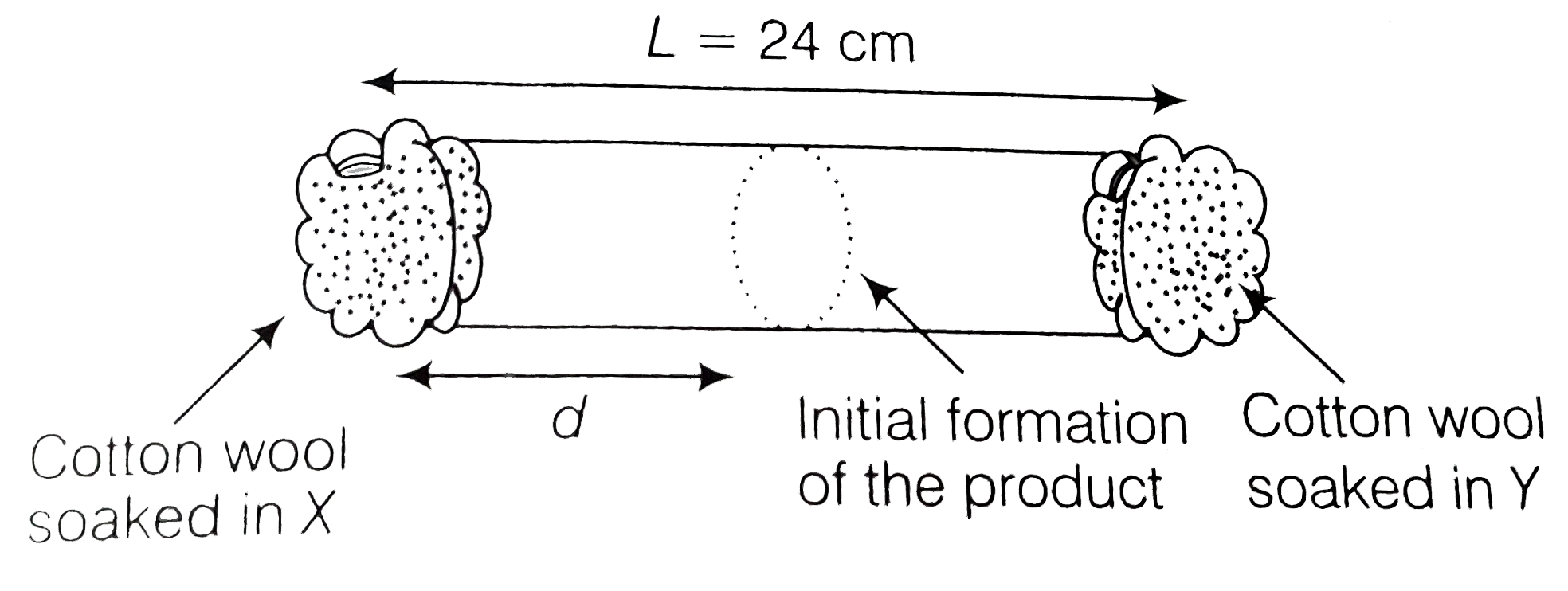
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
STATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Straight Objective Type (MCQ)|29 VideosSTATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Assertion and Reason|11 VideosSTATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Comphension 3|5 VideosSTATES OF MATTER (SOLID STATE CHEMISTRY)
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise ULTIMATE PREPARATORY PACKAGE|21 VideosSTRUCTURE OF ATOM
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Reason Type Questions|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems