Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES & TECHNIOUES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise CONCEPT BASED QUESTION|45 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY - SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES & TECHNIOUES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise VALUE BASED QUESTION|3 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY - SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES & TECHNIOUES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise N.C.E.R.T.|40 VideosNUCLEAR AND RADIO CHEMISTRY
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Evaluate Yourself|45 VideosP BLOCK ELEMENTS (GROUP 13 AND 14 )
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Straight obj.|17 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DINESH PUBLICATION-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES & TECHNIOUES-SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
- Draw the possible resonance for CH(3)- underset(..)overset(..)(O)-over...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following ions is more stable ?
Text Solution
|
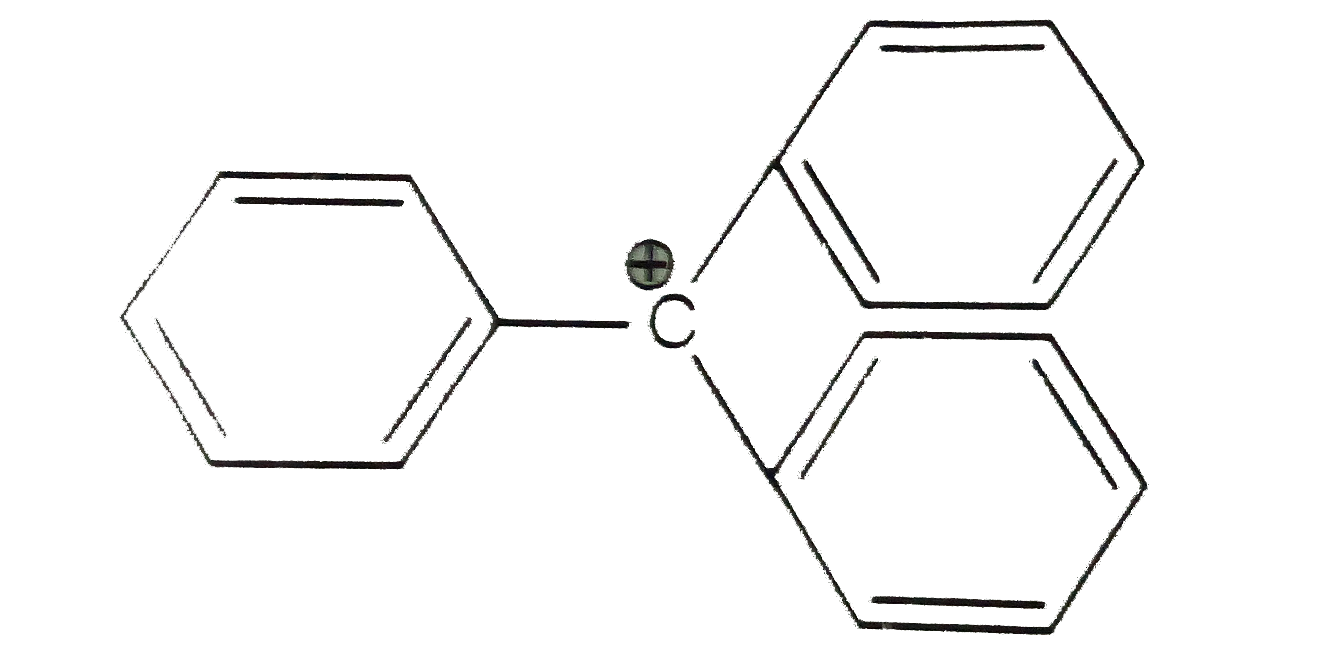
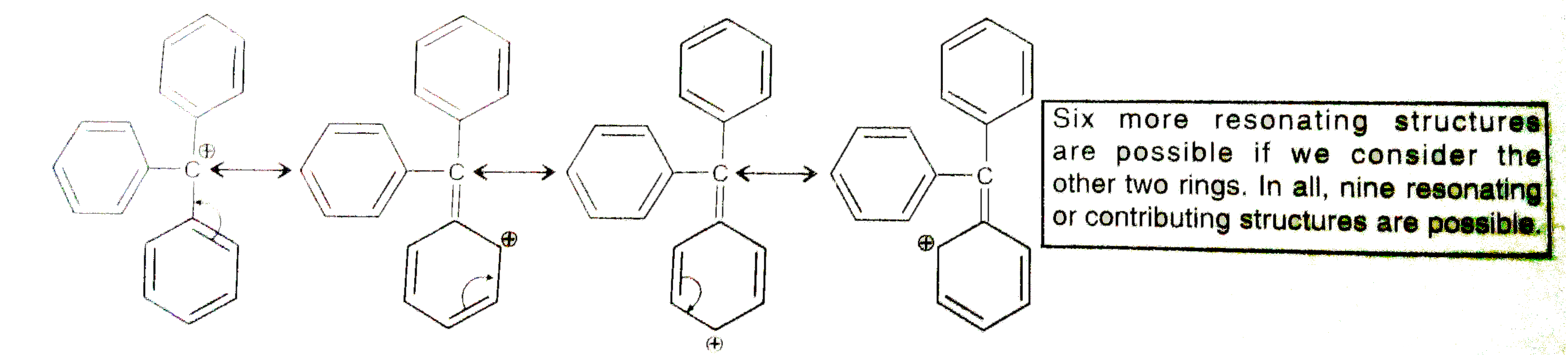
- The structure of triphenylmethyl cation is given below. This is very s...
Text Solution
|
- Write structures of various carbocations that can be obtained from 2-m...
Text Solution
|
- Three students, Manish, Ramesh and Rajini were determining the extra e...
Text Solution
|
- Name the compounds whose line formulae are given below :
Text Solution
|
- Write structural formulae for compounds named as (a) 1-Bromoheptane ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonance structure of the following compounds : (i) CH(2)=...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the most stable species in the following set of ions giving r...
Text Solution
|
- Given three points of differences between inductive effect and resona ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds will not exist as resonance hybrid. G...
Text Solution
|
- Why does SO(3) act as an electrophile ?
Text Solution
|
- Resonance structures of propenal are given below. Which of these reson...
Text Solution
|
- By mistake, an alcohol (boiling point 97^(@)C ) was mixed with a hydro...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the two structures (A) and (B) given below is more stabilised...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by hybridisation ? Compound CH(2)=C=CH(2) contains sp or...
Text Solution
|
- Benzoic acid is an organic compound. Its crude sample can be purified ...
Text Solution
|
- Two liquids (A) and (B) can be separated by the method of fractional d...
Text Solution
|
- You have the mixture of three liquids (A), (B) and (C). There is a lar...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a diagram of bubble plate type fractionating column. When do we r...
Text Solution
|