Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTION FROM BOARD EXAMINATION|77 VideosALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS|8 VideosALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT Exercise|23 VideosALDEHYDES AND KETONES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Interger|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DINESH PUBLICATION-ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS-ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT QUESTION
- At room temperature tertiary alcohols form white turbidity very fast w...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the product of the reaction between HBr and but -2-en-1-ol.
Text Solution
|
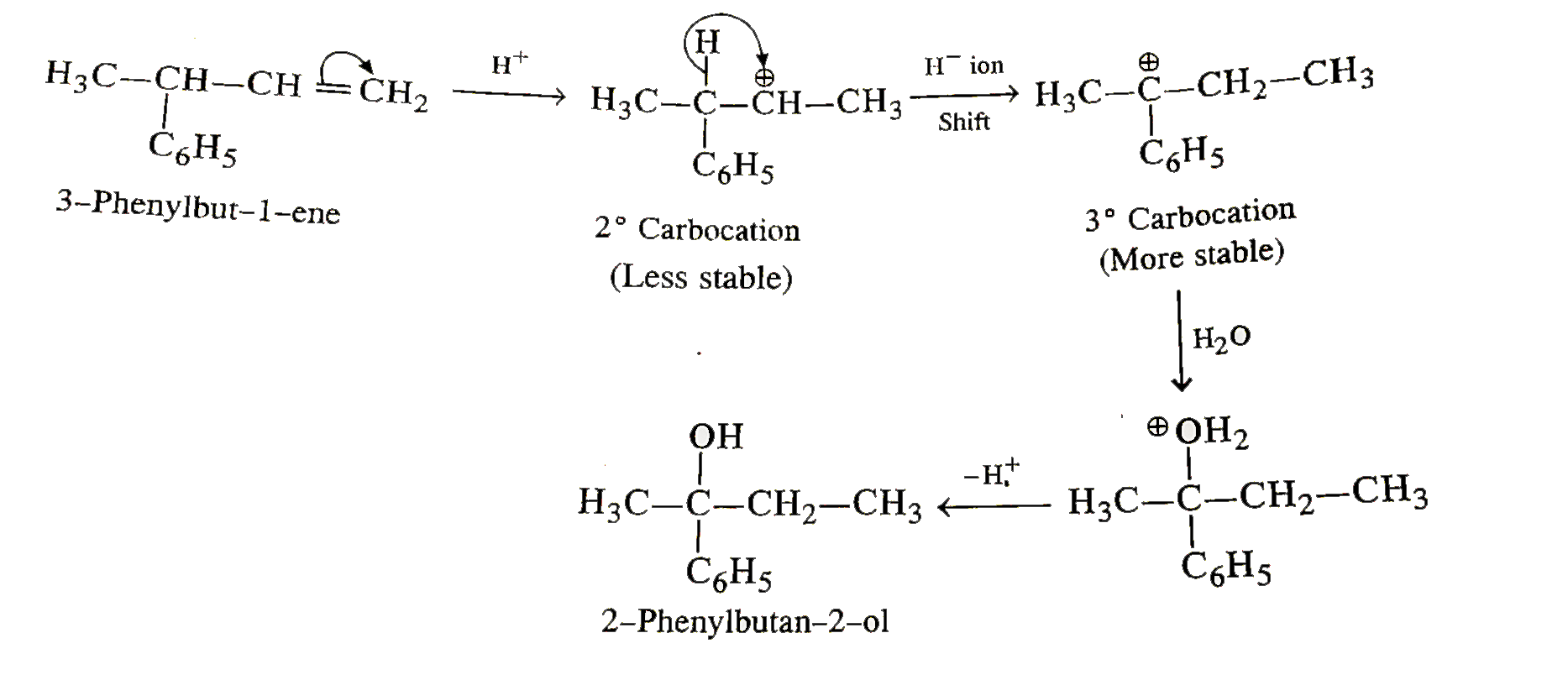
- Hydration of 3-phenylbut-1-ene in dilute H(3)SO(4) forms 2-pheylbutan ...
Text Solution
|
- When t-butanol and n-butanol are separately treated with a few drops o...
Text Solution
|
- 3,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol losses a molecule of water in the presence of c...
Text Solution
|
- What is the structure of the major product when 3-ethylpent -2-ene is ...
Text Solution
|
- p-nitrophenol is a stronger acid than phenol while p-cresol is a weake...
Text Solution
|
- How do you account for the fact that unlike phenol, 2, -dinitrophenol ...
Text Solution
|
- Alcohols react with halogen acids as well as phosphorus halides to for...
Text Solution
|
- The order of reactivity of alcohols in the esterification reaction is ...
Text Solution
|
- Dehydration of alcohol to form an alkene is always carried out with co...
Text Solution
|
- Why is phenol acidic and hexanol neutral towards solution of NaOH ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is the most reactive towards attack by an elect...
Text Solution
|
- Why is cyclohexanol more soluble in water than hexan-1-ol ?
Text Solution
|
- How will you distinguish between CH(3)(CH(2))(3)OH and CH(3)CH=CHCH(2)...
Text Solution
|
- Why can not anhydrous calcium chloride be used for drying ethyl alcoho...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when propan-1-ol is treated with ethanoic acid in the pre...
Text Solution
|
- How will you distinguish between allyl alcohom and n-propyl alcohol ?
Text Solution
|
- Give the product of reaction of ethyl alcohol with conc. H(2)SO(4) at ...
Text Solution
|
- Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between : (i) Ethanol and...
Text Solution
|