Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-GRAVITATION-Long Answer type question
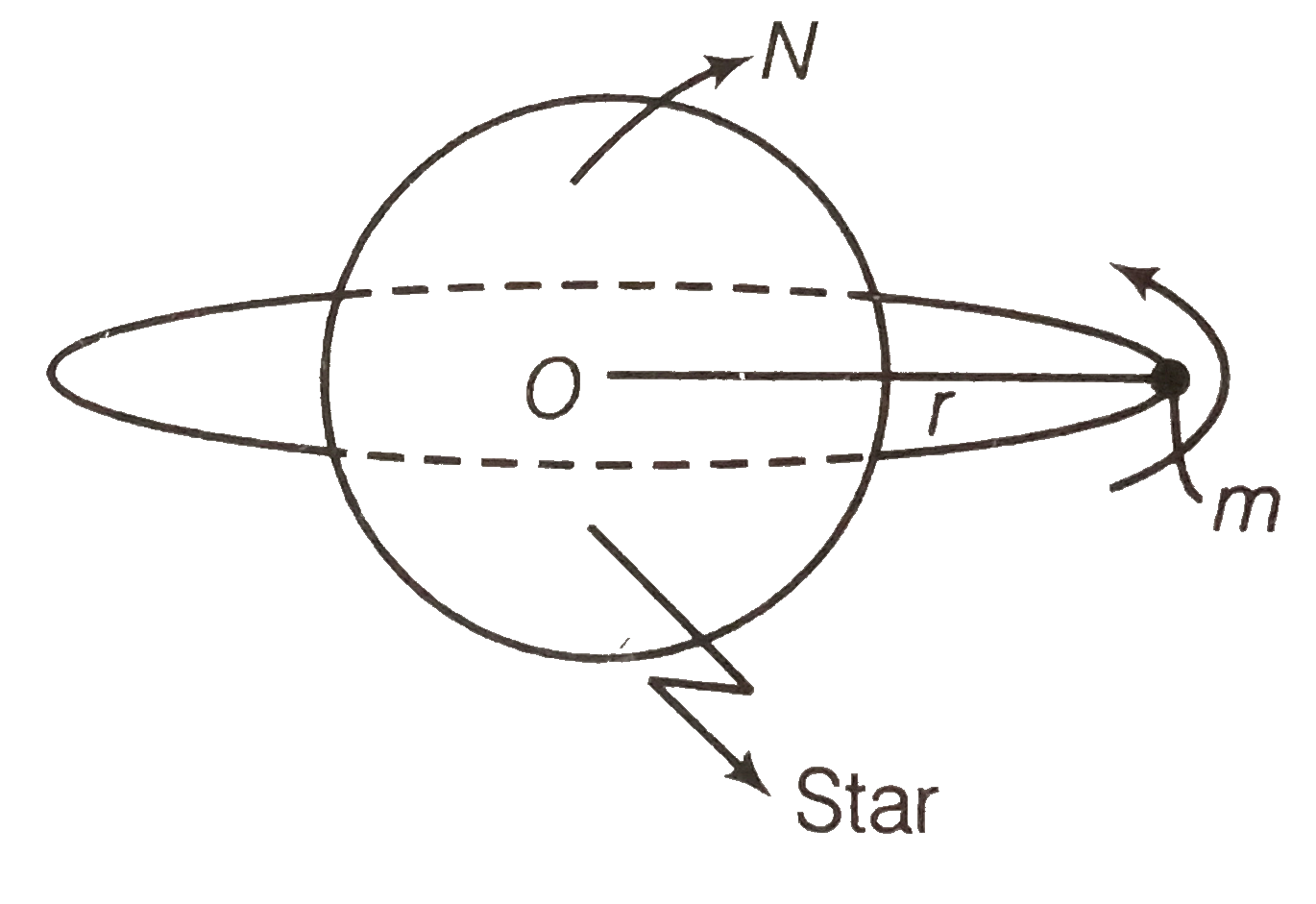
- A star like the sun has serveral bodies moving around it at different ...
Text Solution
|
- Six point masses of mass m each are at the vertices of a regular hexag...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite is to be placed in equatorial geostationary orbit around e...
Text Solution
|
- Earth's orbit is an ellipse with eccentricity 0.0167. Thus, the earth'...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite is in an elliptical orbit around the earth with aphelion o...
Text Solution
|