Text Solution
Verified by Experts
NCERT EXEMPLAR-GRAVITATION-Short Answer type question
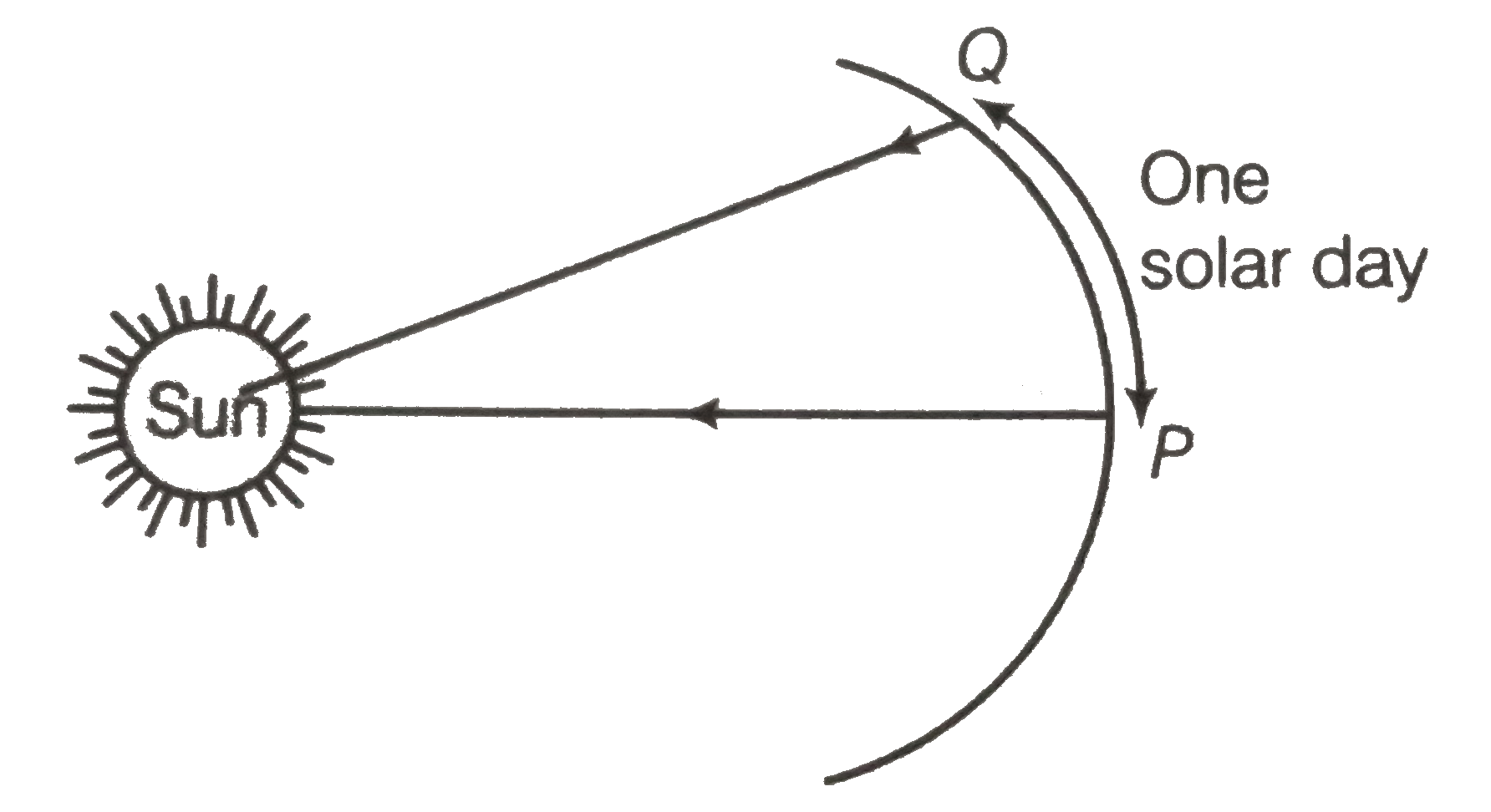
- Mean solar day is the time interval between two successive noon when s...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical heavy spheres are separated by a distance 10 times their...
Text Solution
|
- Show the nature of the following graph for a satellite orbiting the ea...
Text Solution
|
- Shown are several cuves (fig. (a), (b), (c), (d), (e), (f)]. Explain w...
Text Solution
|
- An object of mass m is raised from the surface of the earth to a heigh...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m is placed at P a distance h along the normal through the cent...
Text Solution
|