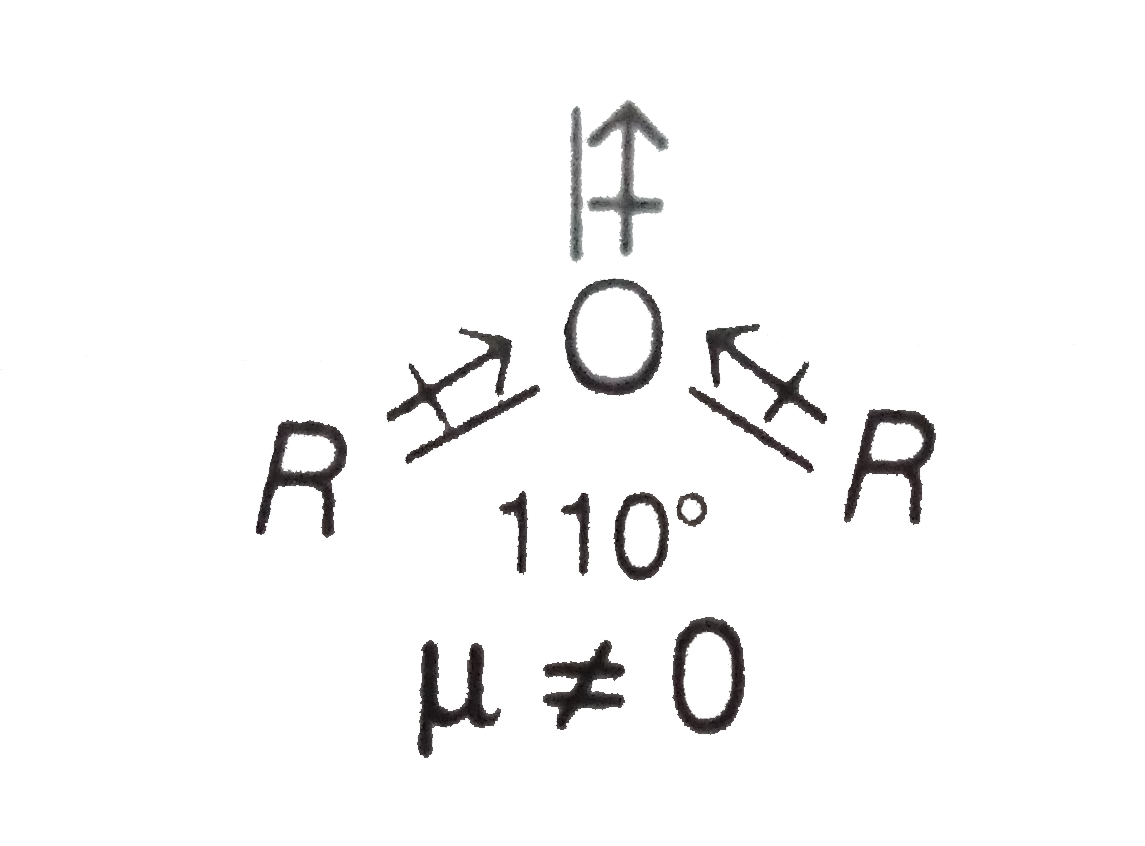Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS-Alcohols, Phenols And Ethers
- Explain why nucleophilic substitution reactions are not very common in...
Text Solution
|
- Preparation of alcohols from alkenes involves the electrophilic attack...
Text Solution
|
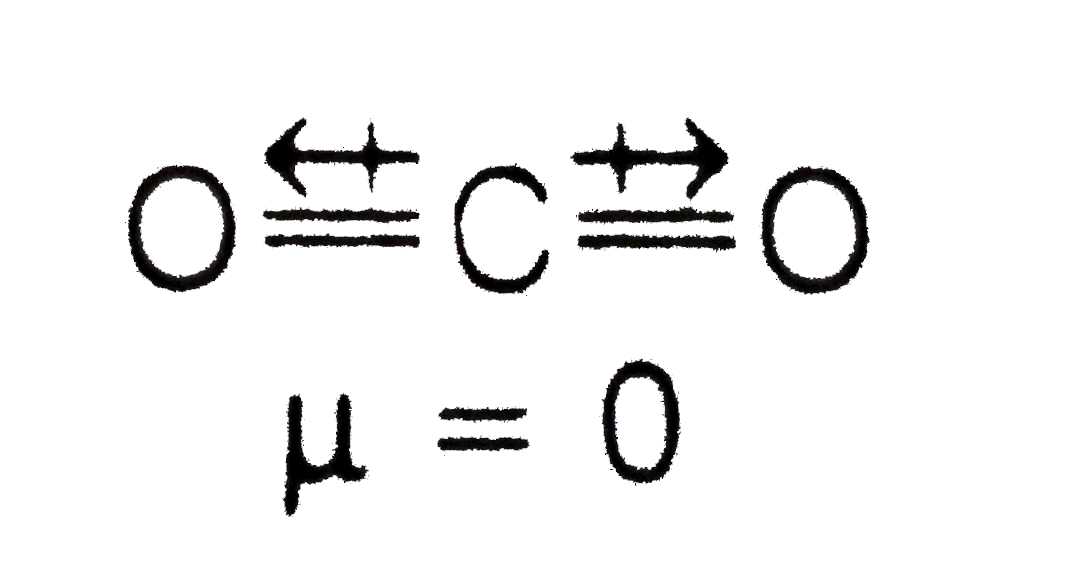
- Explain why is O=C=O non polar while R-O-R is polar ?
Text Solution
|
- Why is the reactivity of all the three classes of alcohols with conc. ...
Text Solution
|
- Write steps to carry out the conversion of phenol to aspirin.
Text Solution
|
- Nitration is an example of aromatic electrophilic substitution and its...
Text Solution
|
- In Kolbe's reactio insteaded of phenol, phenoxide ion is treated with ...
Text Solution
|
- Dipole moment of phenol is smaller than that of methanol. Why ?
Text Solution
|
- Ethers can be prepared by Williamson synthesis in which an alkyl halid...
Text Solution
|
- Why is the C-O-H bond angle in alcohols slightly less than the tetrahe...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why low molecular mass alcohols are soluble in water ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain why p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain why alcohols and ethers of comparable molecular mass have diff...
Text Solution
|
- The carbon-oxygen bond in phenol is slightly stronger than that in met...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange water, ethanol and phenol in increasing order of acidity and g...
Text Solution
|
- Match the structures of the compounds given in Column I with the name ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the starting material given in Column I with the products formed...
Text Solution
|
- Match the items of Column I with items of Column II.
Text Solution
|
- Match the items of Column I with items of Column II.
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) Addition reaction of water to but-1-ene in acidic medium...
Text Solution
|