A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
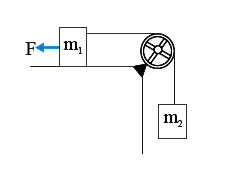
- A constant force F = m(2)g//2 is applied on the block of mass m(1) as ...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks of masses m(1), m(2) and M are arranged as shown in figur...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र में दिखाए गए m(1) द्रव्यमान वाले गुटके पर एक नियत बल F=(m(2)g)/(...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses m(1) and m(2) ( m(2) gt m(1)) are hanging vertically over f...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of mass m(1) and m(2) lie on smooth horizontal table in co...
Text Solution
|
- Pulleys are ideal and string are massless. The masses of blocks are m(...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses m(1) and m(2) are placed on a smooth horizontal surface and...
Text Solution
|
- [" Two masses "m(1)" and "m(2)" are "],[" connected by means of a "],[...
Text Solution
|
- A constant force F = m(2)g//2 is applied on the block of mass m(1) as ...
Text Solution
|