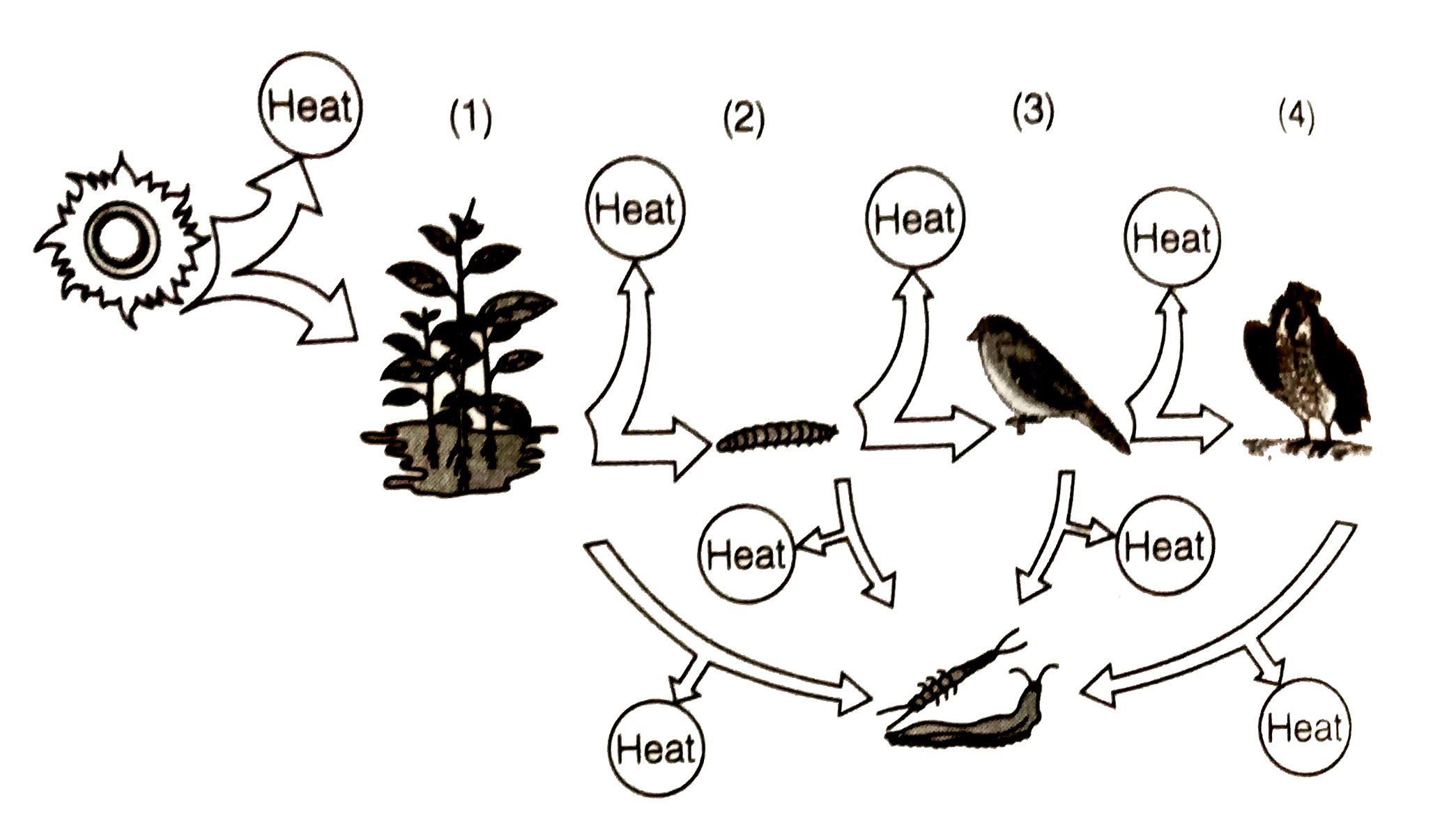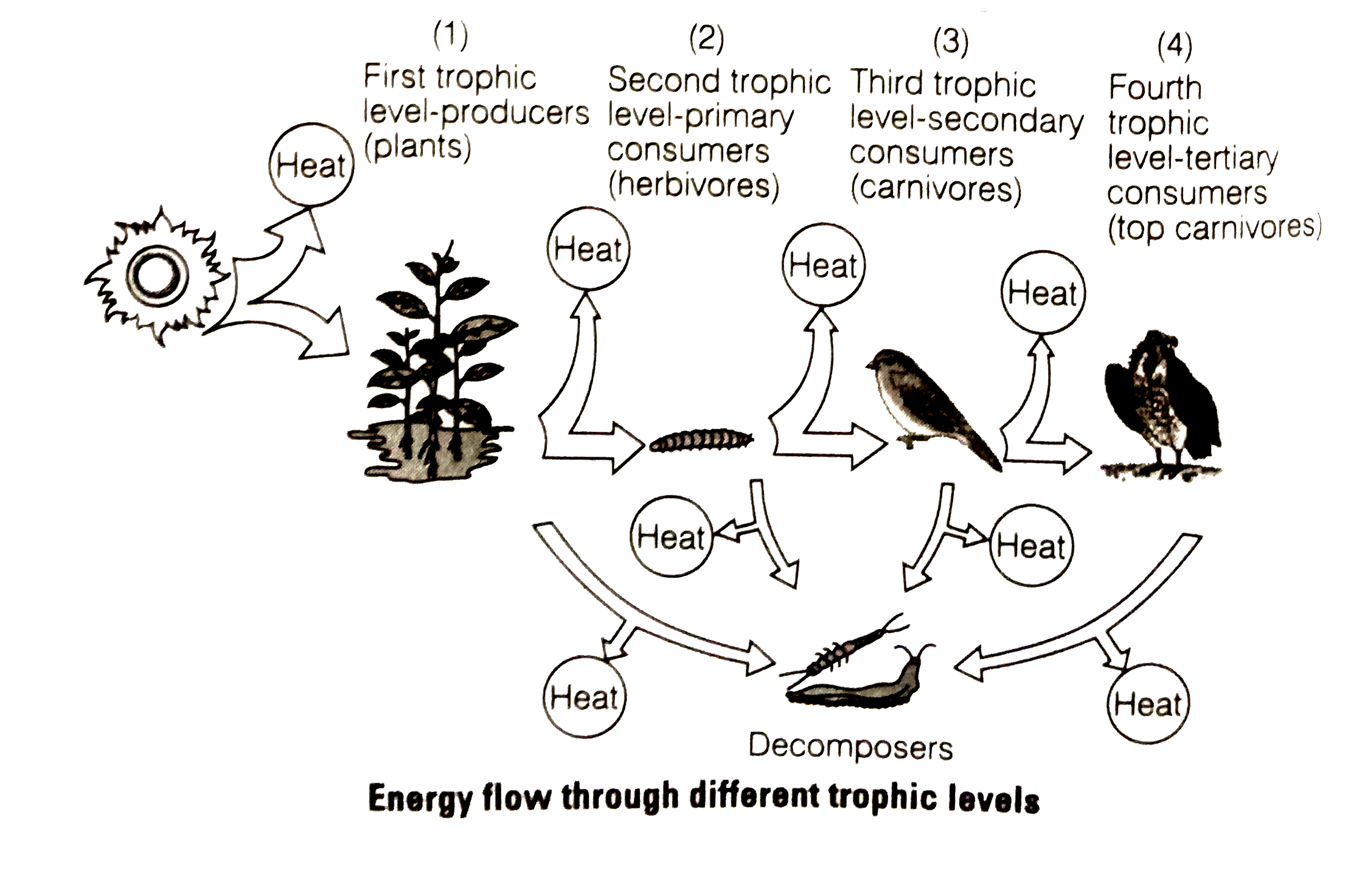Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-ECOSYSTEM-Ecosystem
- In relation to energy transfer in ecosystem, explain the statement ”10...
Text Solution
|
- Primary productivity caries from ecosystem to ecosystem. Explain ?
Text Solution
|
- Sometimes due to biotic/abiotic factor the climax remain in a particul...
Text Solution
|
- What is an incomplete ecosystem? Explain with the help of suitable exa...
Text Solution
|
- What are the shortcomings of ecological pyramids in the study of ecosy...
Text Solution
|
- How do you distinguish between humification and mineralisation?
Text Solution
|
- Fill in the trophic levels (1,2,3 and 4) in th eboxes provided in the ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of decomposition of detritus is affected by the abiotic facto...
Text Solution
|
- A farmer harvests his crop and expresses his harvest in three differen...
Text Solution
|
- Justify the following statement in terms of ecosystem dynamics. "Natur...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following ecosystems will be more productive in terms at:...
Text Solution
|
- What are the three types of ecological pyramids. What information is c...
Text Solution
|
- Write a short note on pyramid of numbers and pyramid of biomass.
Text Solution
|
- Given below is a list of autotrophs and heterotrophs. With your knowle...
Text Solution
|
- ”The energy flow in the ecosystem follows the second law of thermodyna...
Text Solution
|
- What will happen to an ecosystem if (a) All producers are removed ...
Text Solution
|
- Give two examples of artificial or man made ecosystems. List the salie...
Text Solution
|
- The biodiversity increases when one moves from the pioneer to the clim...
Text Solution
|
- What is a biogeochemical cycle. What is the role of the reservoir in a...
Text Solution
|
- What will be the P/R ratio of a climax community and a pioneer communi...
Text Solution
|