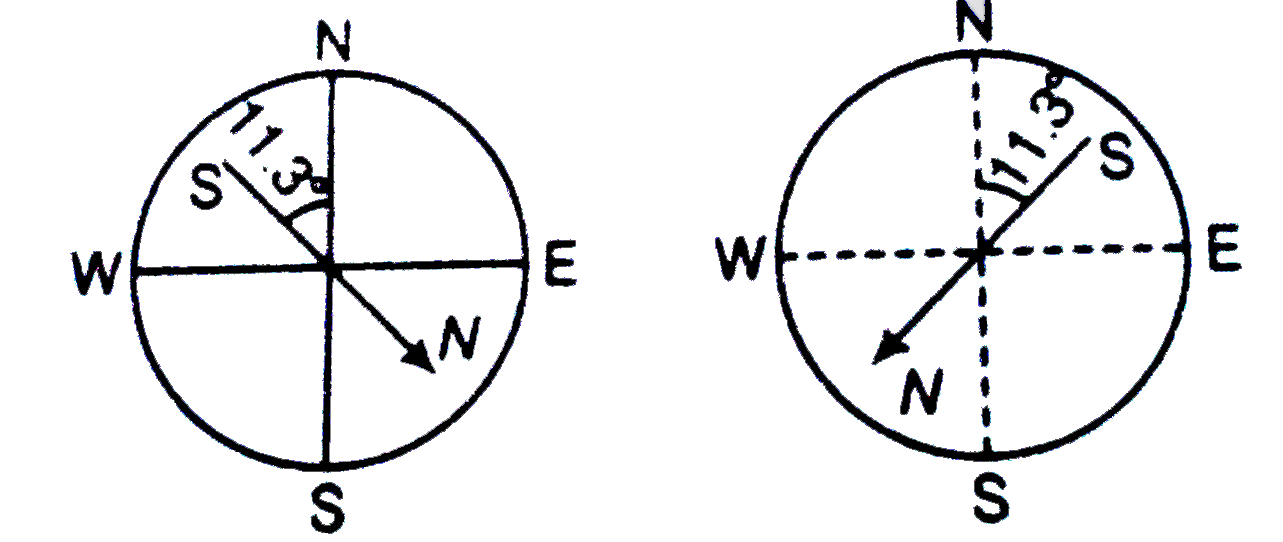A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-MAGNETISM AND MATTER -Magnetism And Matter
- A toroid of n turns, mean radius R and cross-sectional radius a carrie...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field of the earth can be modelled by that of a point dip...
Text Solution
|
- In a permanent magnet at room temperature.
Text Solution
|
- Consider the two idealized systems: (i) a parallel plate capacitor wit...
Text Solution
|
- A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of 8Am^-1 when placed ...
Text Solution
|
- S is the surface of a lump of magnetic material.
Text Solution
|
- The primary origin(s) of magnetism lies in
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid has 1000 turns per metre and carries a current of 1A. ...
Text Solution
|
- Essential difference between electrostatic shielding by a conducting s...
Text Solution
|
- Let the magnetic field on earth be modelled by that of a point magnet...
Text Solution
|
- A proton has spin and magnetic moment just like an electron. Why then ...
Text Solution
|
- A permanent magnet in the shape of a thin cylinder of length 10 cm has...
Text Solution
|
- Explain quantitatively the order of magnitude difference between the d...
Text Solution
|
- From molecular view point, discus the temperature dependence of suscep...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of superconducting material is dipped in liquid nitrogen and pl...
Text Solution
|
- Verify the Gauss's law for magnetic field of a point dipole of dipole ...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical bar magnets are rivetted together at centre in the sam...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose we want to verify the analogy between electrostatic and magnet...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet of magnetic moment M and moment of inertia I (about centr...
Text Solution
|
- Use i the Ampere's law for H and ii continuity of lines of B, to concl...
Text Solution
|