Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
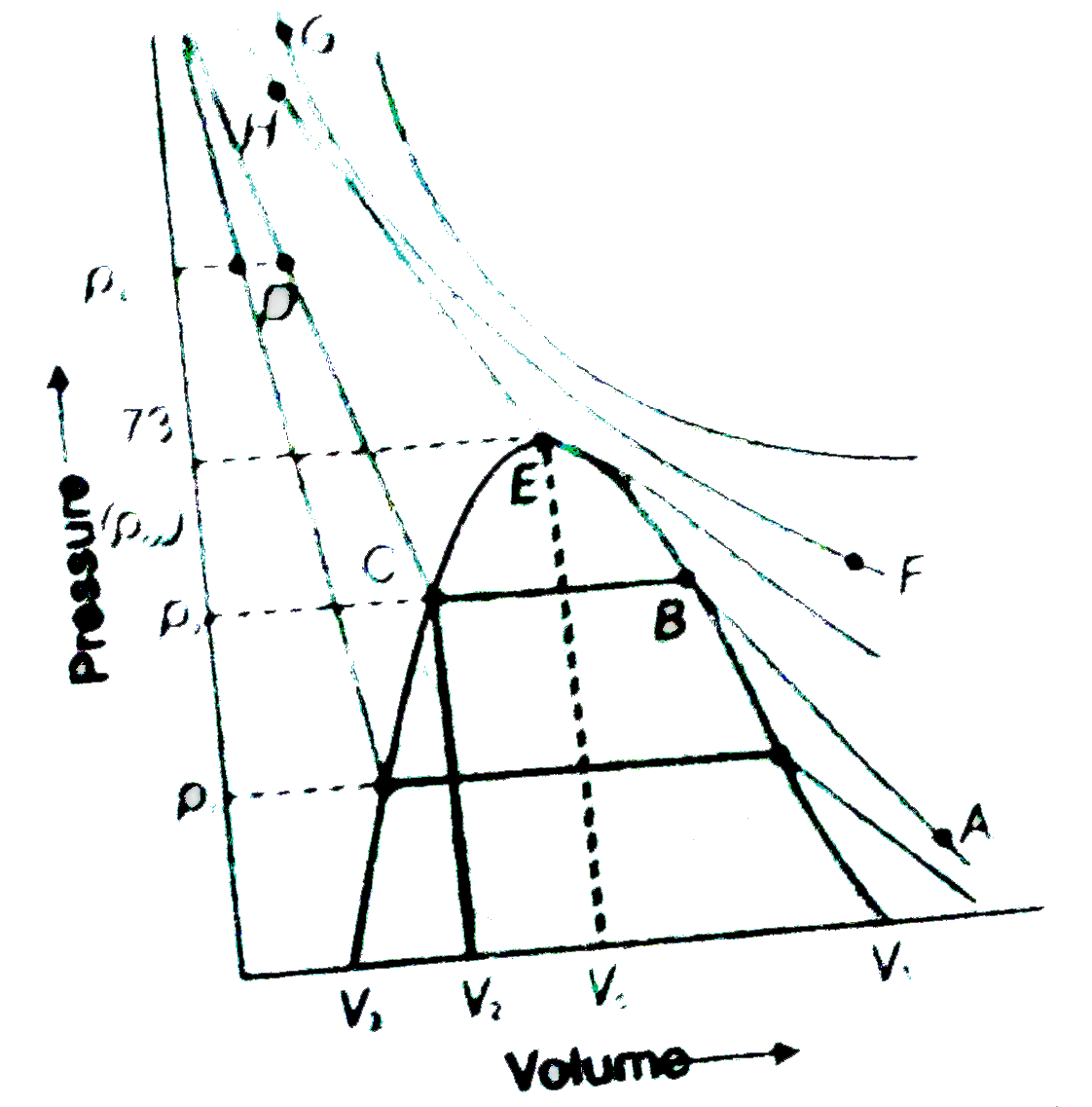
NCERT EXEMPLAR-STATES OF MATTER-Long Answer Type Question
- The average velocity of CO(2) at the temperature T(1)K and maximum (mo...
Text Solution
|
- The variation of vapour of different liquids with temperature is shown...
Text Solution
|
- Why does the boundary between liquid phase and gaseous phase disappear...
Text Solution
|
- Why does sharp glass edge become smooth on heating it upto its melting...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the term 'laminar flow'. Is the velocity of molecules same in ...
Text Solution
|
- Carbon dioxide unusual because it has no liquid phase at normal atmos...
Text Solution
|