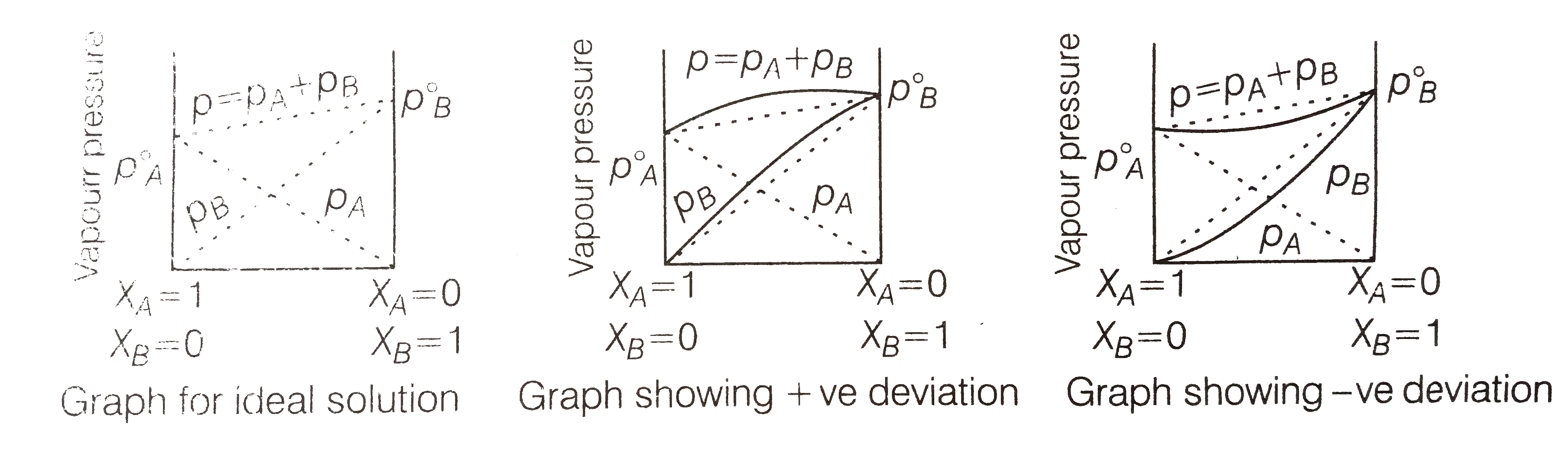Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-SOLUTIONS -Solutions
- Why is the vapous pressure of an aqueous solution of gulucose lower th...
Text Solution
|
- How does sprinking of salt help in clearing the snow covered roads in ...
Text Solution
|
- What is "esmipermeble membrane"?
Text Solution
|
- Give an example of a material used for makin gsemipermeable membrance ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following Columns
Text Solution
|
- Match the following Columns
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following order is correct?
Text Solution
|
- Match the following columns
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) Molarity of a solution in liquid state changes with temp...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) When methyl alcohol is added to water, boiling point of ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) When NaCl is added to water a depression in freezing poi...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) When solution is separated from the pure solved by a sem...
Text Solution
|
- Diffine the following mofes of expressing the concentration of a solut...
Text Solution
|
- Using Raoult's Law explain how the total vapour pressure over the solu...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the terms ideal and non-idealsolution in the light of forces o...
Text Solution
|
- Why is it not possible to obtain pure ethanol by fractional distillati...
Text Solution
|
- When kept in water, raisin swells in size. Name and explain the phenom...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss biological and industrial applications of osmosis.
Text Solution
|
- How can you remove the hard calcium carbonate layer of the egg without...
Text Solution
|
- Why is the mass determined by measuring a colligative property in case...
Text Solution
|