Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-P-BLOCK ELEMENTS-P-Block Elements
- PH(3) forms bubbles when passed slowly in water but NH(3) dissolves. E...
Text Solution
|
- In PCl(5) phosphorus is in sp^(3) d hybridised state but all its five ...
Text Solution
|
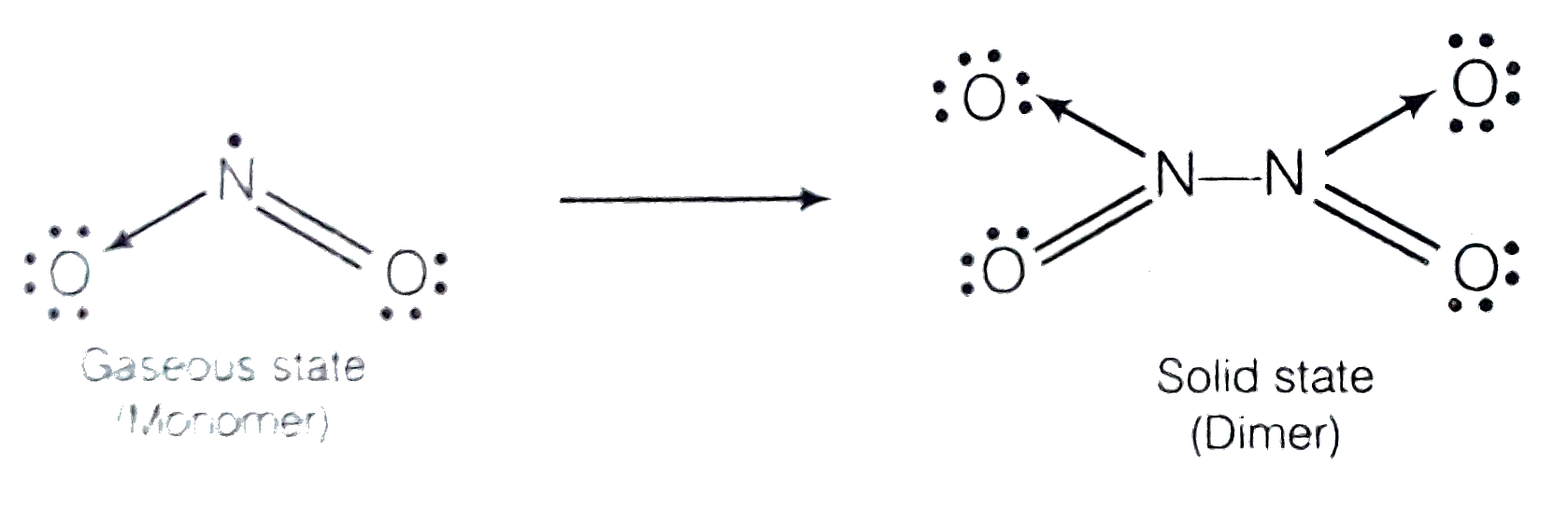
- Why is nitric oxide paramagnetic in gaseous state but the solid obtain...
Text Solution
|
- Give one reason to explain why ClF(3) exists but FCl(3) does not exist...
Text Solution
|
- Out of H(2)O which one has higher bond angle and why?
Text Solution
|
- SF(6) is known but SC(6) is not. Why?
Text Solution
|
- On reaction with Cl(2) phosphorus forms two types of halides 'A' and '...
Text Solution
|
- In the ring test of NO(3)^(-) ion, Fe^(2+) ion reduces nitrate ion to ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why the stability of oxoacids of chlorine increases in the ord...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why ozone is thermodynamically less stable then oxygen ?
Text Solution
|
- P(4)O(6) reacts with water according to equation P(4)O(6)to4H(3)PO(3)....
Text Solution
|
- White phosphorus reacts with chlorine and the product hydrolyses in th...
Text Solution
|
- Name three oxoacids of nitrogen. Write the disproportionation reaction...
Text Solution
|
- Nitric acid forms an oxide of nitrogen on reaction with P(4)O(10). Wri...
Text Solution
|
- (i) White phosphorus (ii) red phosphorus and (iii) black phosphorus. W...
Text Solution
|
- Given an example to show the effect of concentration of nitric acid on...
Text Solution
|
- PCl(5) reacts with finely divided silver on heating and a white silver...
Text Solution
|
- Phosphorus forms a number of oxoacids. Out of these oxoacids, phosphin...
Text Solution
|
- Match the compounds given in Column I with the hybridisation and shape...
Text Solution
|
- Match the formulas of oxides given in Column I with the type of oxide ...
Text Solution
|