Join CA and CB.
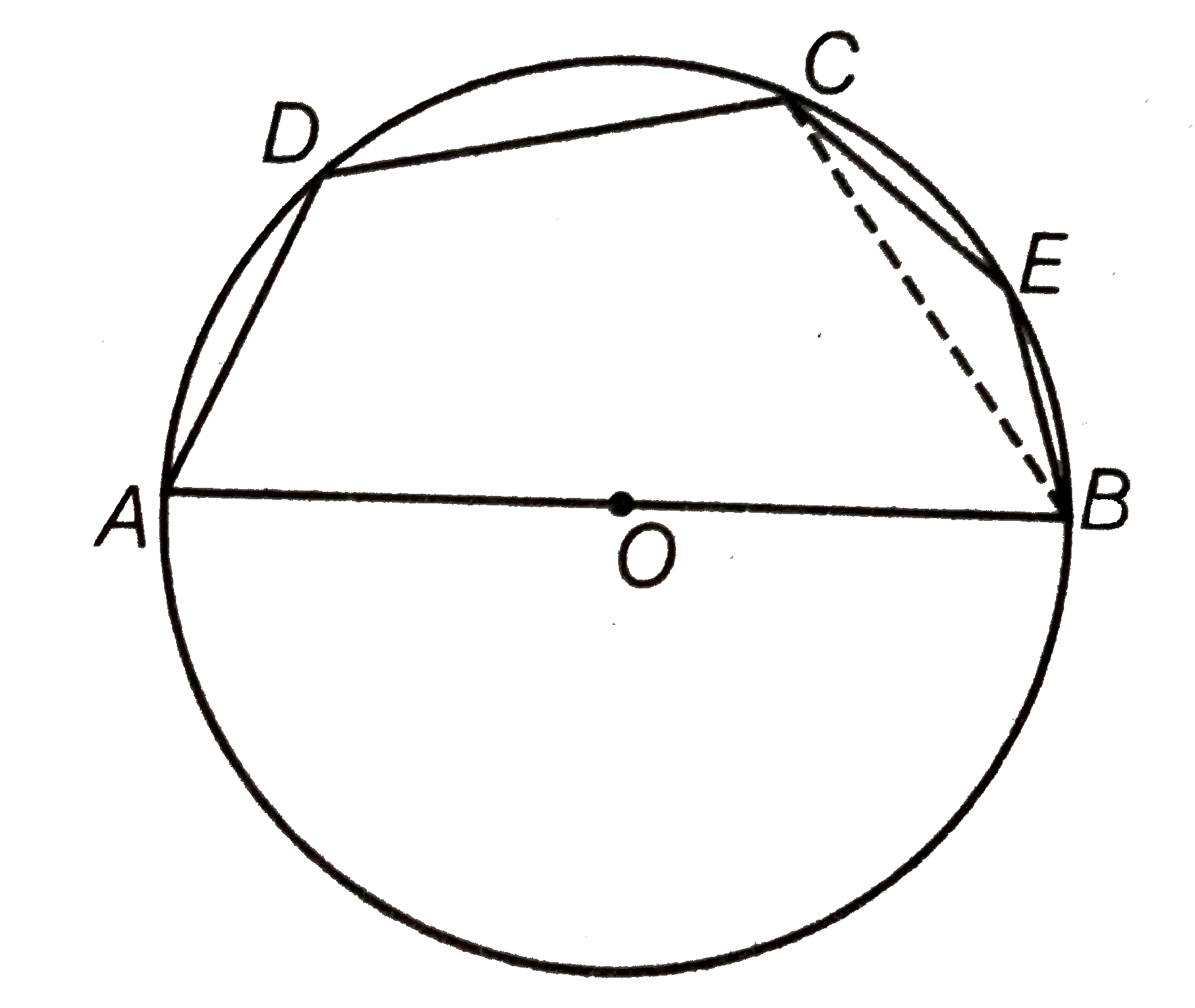
Since, ADCB is a cyclic quadrilateral.
`:. angleADC+angleCBA=180^(@)`.
[sum of opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral is `180^(@)`]
`rArr angleCBA=180^(@)-120^(@)=60^(@) [:'angleADC=120^(@)]`
`"In" DeltaACB, angleCAB+angleCBA+angleACB=180^(@)`
[by angle sum property of a triangle]
`:. angleCAB+60^(@)+90^(@)=180^(@)`
[triangle formed from diameter to the circle is `90^(@) i.e.,angleACB=90^(@)`]
`rArr angleCAB=180^(@)-150^(@)=30^(@)`