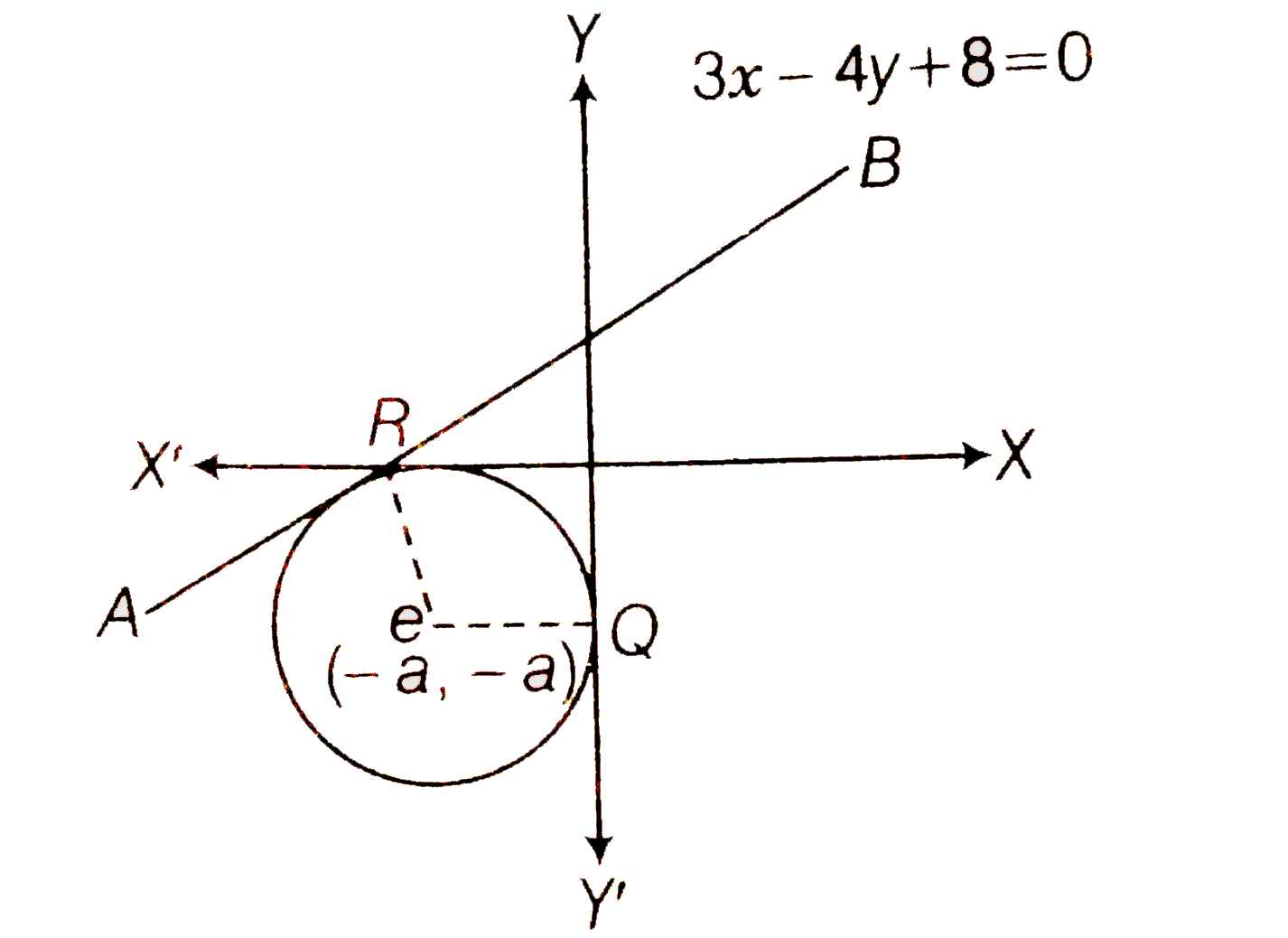A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-CONIC SECTIONS-Objective type
- Find the equation of the circle which touches both the axes and the li...
Text Solution
|
- The area of the circle centred at (1,2) and passing through (4,6) is
Text Solution
|
- Equation of a circle which passes through (3,6) and touches the axes i...
Text Solution
|
- Equation of the circle with centre on the y-axis and passing through t...
Text Solution
|
- Find the equation of a circle with origin as centre and which circumsc...
Text Solution
|
- If the focus of a parabola is (0,-3) and its directrix is y=3, then it...
Text Solution
|
- If the parabola y^2=4a x\ passes through the point (3,2) then find th...
Text Solution
|
- If the vertex of a parabola is the point (-3,0) and the directrix is t...
Text Solution
|
- If question of the ellipse whose focus is (1,-1), then directrix the l...
Text Solution
|
- The length of the latusrectum of the ellipse 3x^(2)+y^(2)=12 is
Text Solution
|
- If e is eccentricity of the ellipse (x^(2))/(a^(2))+(y^(2))/(b^(2))=1(...
Text Solution
|
- The eccentricity of the hyperbola whose length of the latus rectum is ...
Text Solution
|
- The distance between the foci of a hyperbola is 16 and its eccentricit...
Text Solution
|
- Equation of the hyperbola with eccentricity 3/2 and foci at (±2,0) is
Text Solution
|