A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-ELASTICITY-Chapter Exercise
- A rubber pipe of density 1.5 xx 10^(3) N//m^(2) and Young's modulus 5 ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given Fig. 7(CF).2, if the dimensions of the two wires are the ...
Text Solution
|
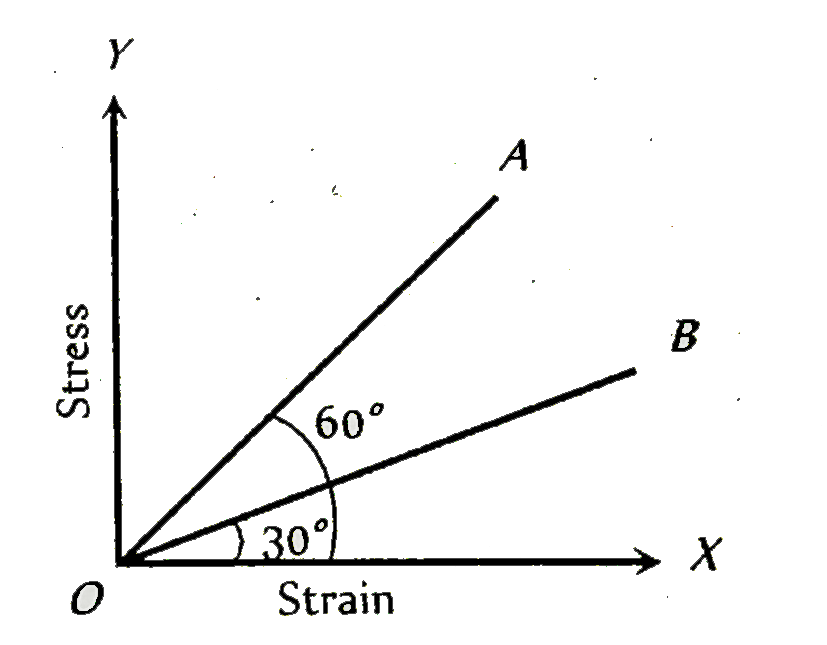
- The stress versus strain graphs for wires of two materials A and B are...
Text Solution
|
- An elevator cable is to have a maximum stress of 7xx10^(7) Nm^(-2) to ...
Text Solution
|
- The following four wires are made of same material. Which of these wil...
Text Solution
|
- A copper wire (Y=10^(11) Nm^(-2)) of length 8 m and a steel wire (Y=2x...
Text Solution
|
- The strain stress curves of three wires of different materials are sho...
Text Solution
|
- The extension in a string obeying Hooke's law is x. The speed of sound...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy U between two molecules as a function of the dist...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram shows a forc-extension graph for a rubber band. Consider...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two cylindrical rods of indentical dimesnions, one of rubber ...
Text Solution
|
- The adjacent graph shows the extension Deltal of a wire of length 1m...
Text Solution
|
- A brass of length 2 m and cross-sectional area 2.0 cm^(2) is attached ...
Text Solution
|
- One end of uniform wire of length L and of weight W is attached rigidl...
Text Solution
|
- The wire of a Young's modules appartus is elongated by 2 mm when a bri...
Text Solution
|
- A rigid bar of mass M is supported symmetrically by three wires each o...
Text Solution
|
- A cord of mass m length L, area of cross section A and Young's modulus...
Text Solution
|
- The density of a metal at normal pressure is rho. Its density when it ...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a long metallic wire of length (L) is tied to the ceiling. ...
Text Solution
|
- The length of an elastic string is a metre when the longitudinal tens...
Text Solution
|