The equivalent circuit can be drawn as under,
`X prop (L)/(R^(4)) " " ( "as" X=(8 eta L)/(pi R^(4)))`
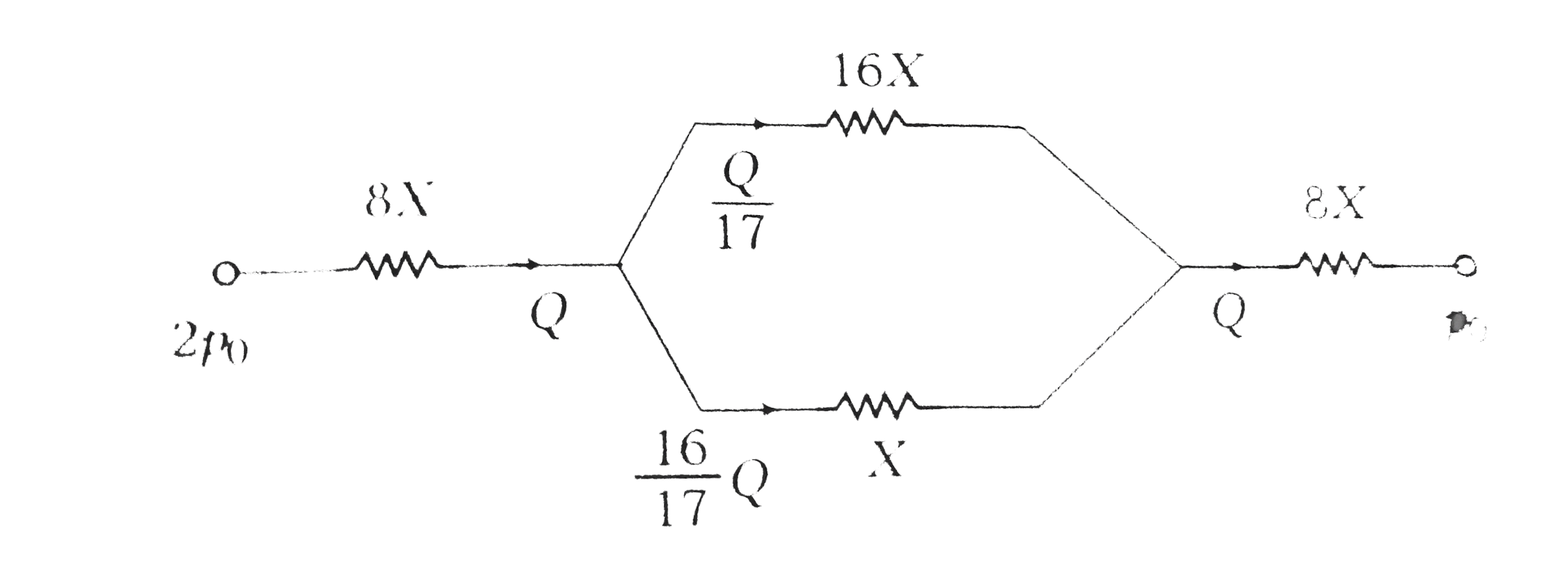
`therefore X_(AB) : X_(CD) : X_(EF) : X_(GH)`
`=((1)/(2))/(((1)/(2))^(4)):(((1)/(2)))/(((1)/(2))^(4)):((1))/((1)/(2))^(4):((1))/((1)^(4))=8:8:16:1`
(a) As the current is distributed in the inverse ration of the resistance (in parallel). The Q will be distributed in the inverse ratio of X.
Thus, volume flow through EF will be `(Q)/(17)` and that from GH will be `(16)/(17)Q`.
(b) ` X_("net")=8X+[((16X)(X))/((16X)+(X))]+8X=(288)/(17)X`
` therefore Q=(Deltap)/(X_("net")) " " (" as" i=(Delta V)/(R ))`
`=((2p_(0)-p_(0)))/((288)/(17)X)=(17p_(0))/(288X)`
Now, let `p_(1)` be the pressure at E, then
`2p_(0)-p_(1)=8 QX=(8xx17 p_(0))/(288)`
`therefore " " p_(1)=(2-(17xx8)/(288)) p_(0)=1.53 P_(0)`
Similarly, if `p_(2)` be the pressure at F, then
`p_(2)-p_(0)=8 QX`
`therefore " " p_(2)=p_(0)+(8xx17)/(288)p_(0) " or " p_(2)=1.47 p_(0)`