Excess pressure inside first soap bubble
`p_(1)=p_(0)+(4T)/(r_(1))`
Excess pressure inside second soap bubble
`p_(2)=p_(0)+(4T)/(r_(2))`
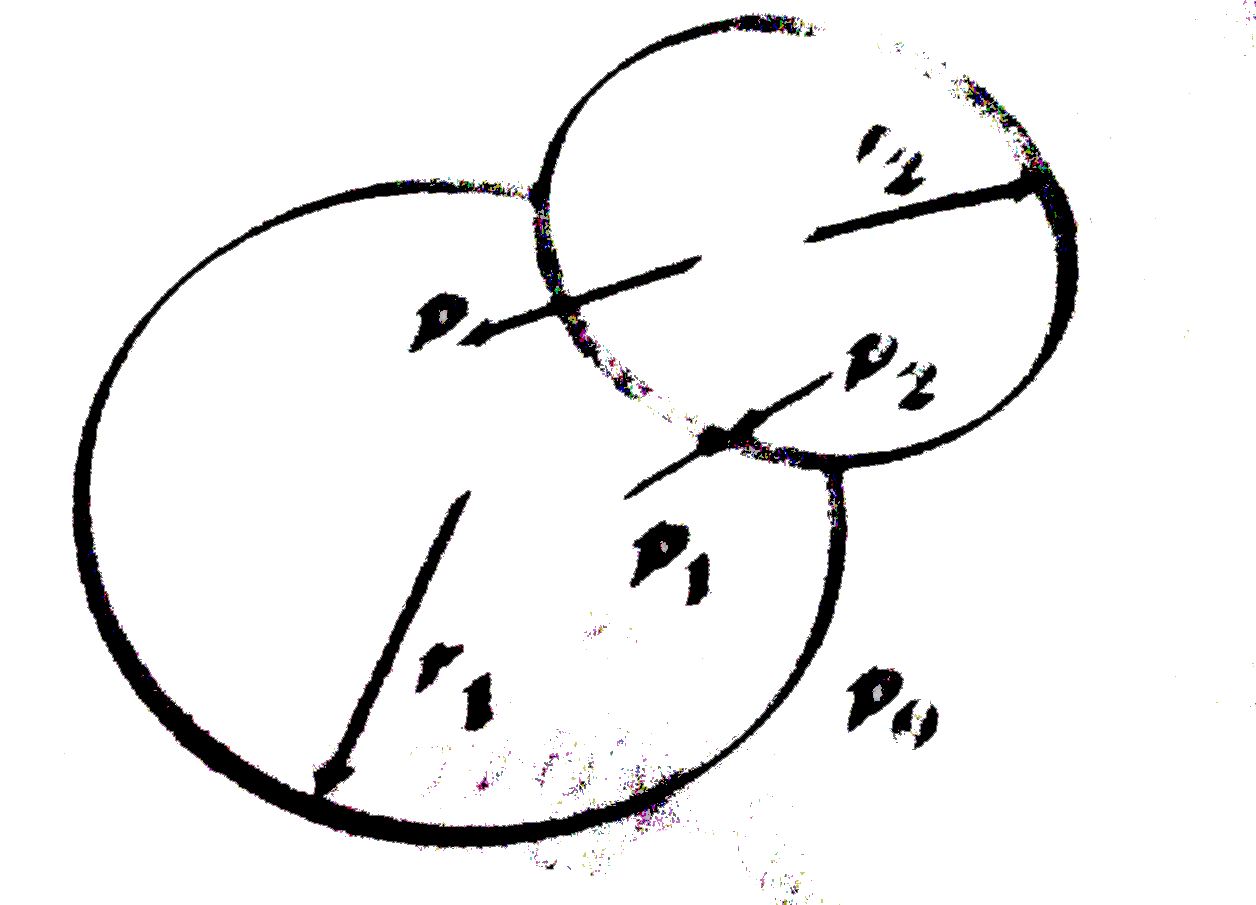
`because " " r_(2) lt r_(1) therefore p_(2) gt p_(1)`
i.e., pressure inside the smaller bubble will be more. The excess pressure
`p=p_(2)-p_(1)=4T((r_(1)-r_(2))/(r_(1)r_(2)))`
This excess pressure acts from concave to convex side, the interface will be concave towards smaller bubble and convex towards larger bubble. Let R be the radius of interface then,
`p=(4T)/(R )`
From Eqs. (i) and (ii),
`R=(r_(1)r_(2))/(r_(1)-r_(2))=((0.004)(0.002))/((0.004-0.002))=0.004 m`