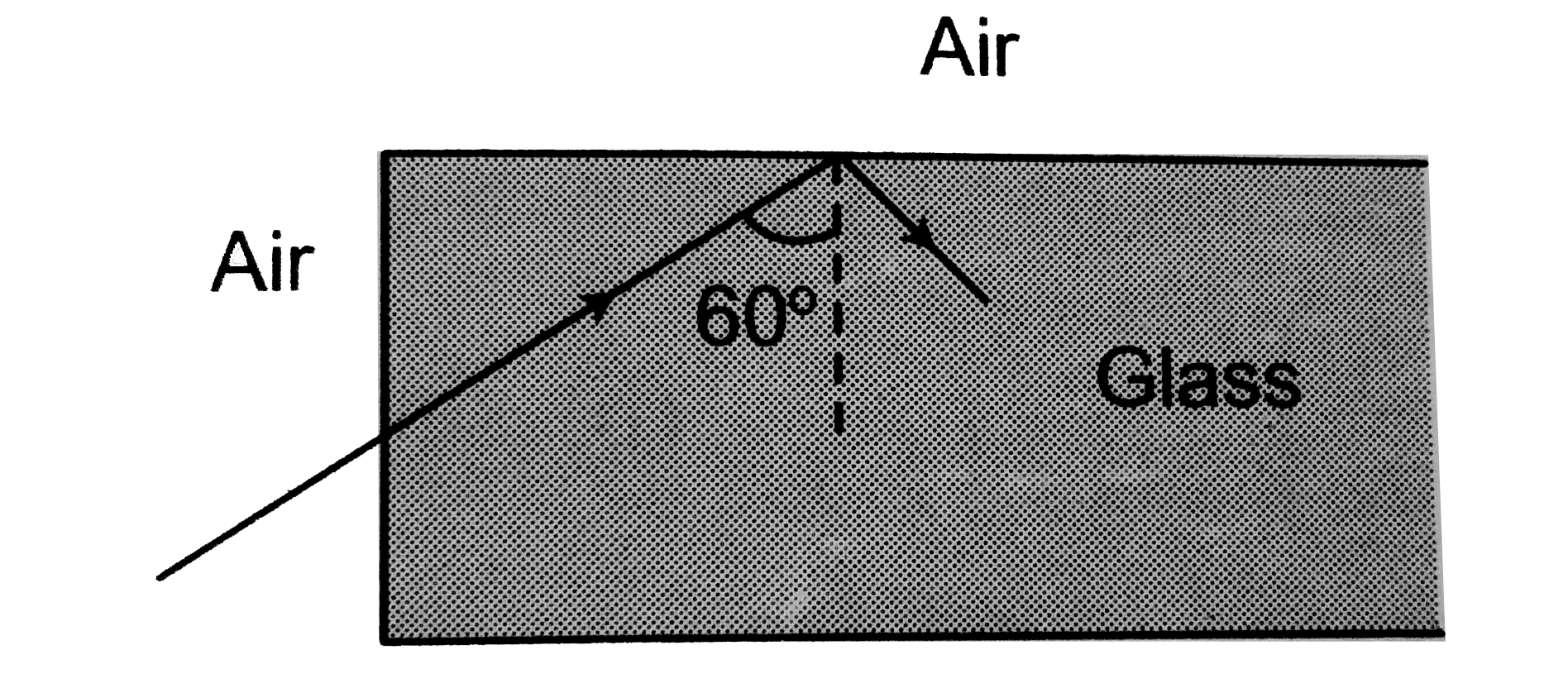
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise medical entrance special format question|25 VideosRAY OPTICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrance gallary|76 VideosRAY OPTICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Checkpoint 9.7|10 VideosNUCLEI
DC PANDEY|Exercise C MADICAL ENTRANCES GALLERY|46 VideosREFLECTION OF LIGHT
DC PANDEY|Exercise Subjective|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-RAY OPTICS-Exercise
- A short linear object of length b lies along the axis of a concave mir...
Text Solution
|
- A mirror is inclined at an angle of theta with the horizontal. If a ra...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray from air is incident (as shown in figure ) at one end of a...
Text Solution
|
- A thin convergent glass lens (mug=1.5) has a power of +5.0D. When this...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows an equi-convex lens. What should be the condition of ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light makes an angle of 10^@ with the horizontal and strikes ...
Text Solution
|
- In the measurement of the angle of a prism using a spectrometer, the r...
Text Solution
|
- A thin rod of length d//3 is placed along the principal axis of a conc...
Text Solution
|
- The graph shown part of variation of v with change in u for a concave ...
Text Solution
|
- When an object is at distances x and y from a lens, a real image and a...
Text Solution
|
- A symmetric doule convex lens is cut in two equal parts by a plane per...
Text Solution
|
- A ray incident at a point at an angle of incidence of 60^(@) enters a ...
Text Solution
|
- The graph in Fig. shows how the inverse of magnification 1//m produced...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 30 cm forms a real image three times lar...
Text Solution
|
- An object is placed at 21 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of...
Text Solution
|
- A thin prism P with angle 4^(@) and made from glass of refractive inde...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens produces an image of a real object on a screen with a ma...
Text Solution
|
- An infinitely long rod lies along the axis of a concave mirror of foca...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror is placed horizontally inside water (mu=4/3). A ray fal...
Text Solution
|
- A point object is moving with a speed v before an arrangement of two m...
Text Solution
|