Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LAW OF MOTION
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS (V Conceptual Question )|16 VideosLAW OF MOTION
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS (VI Numerical Problems)|62 VideosLAW OF MOTION
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS (III Short Answer Question )|42 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS (VI. Conceptual Questions.)|8 VideosMOTION OF SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND BODIES
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWER (NUMERICAL PROBLEMS)|60 Videos
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS-LAW OF MOTION -OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS (IV Long Answer Question )
- Briefly explain how is a vehicle able to go round a leveled curved tr...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the angle of banking so as to minimize the wear and tear ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe galileo experiments concerning motion of object on inclined p...
Text Solution
|
- Explain with example how earth can be treated as both inertial and n...
Text Solution
|
- Write a note on aristotle vs newton's approach on sliding object Ap...
Text Solution
|
- Express Newton's second law of motion in component form. Give its sign...
Text Solution
|
- For the same force heavier mass experience lesser acceleration explai...
Text Solution
|
- Using newton 's laws calculate the tension acting on the mango hagin...
Text Solution
|
- Briefly explain how is a horse able to pull a cart
Text Solution
|
- Explain the meaning of law of conservation of linear momentum
Text Solution
|
- Prove impulse momentum equation
Text Solution
|
- Show how impulse force can be measured graphically
Text Solution
|
- What happens to the object at rest if (i) f(s)=0 (ii) f(s)=f("ext") (i...
Text Solution
|
- Draw and explain the variations of force of friction vs applied force...
Text Solution
|
- List and explain any two application of angle of repose
Text Solution
|
- With an activity prove that coefficent of static friction vaies from ...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for the acceleartion of the body sliding down a ...
Text Solution
|
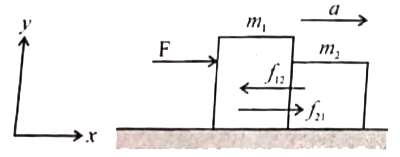
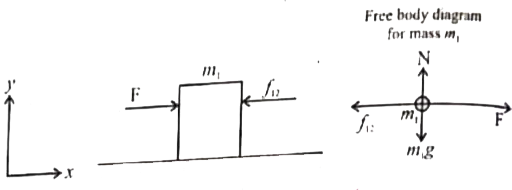
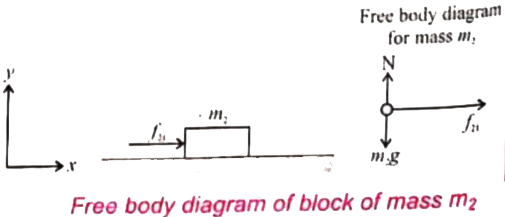
- Two blocks of masses m1 and m2 (m1 gt m2) in contact with each other...
Text Solution
|
- Briefly explain how is a vehicle able to go round a leveled curved tr...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the angle of banking so as to minimize the wear and tear ...
Text Solution
|