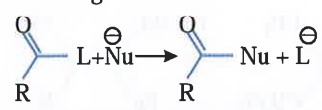
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-CARBONYL COMPOUNDS-LEVEL-V
- The reaction is oxidation - reduction type and takes place in presence...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction is oxidation - reduction type and takes place in presence...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid derivatives contain C= O group. Alde...
Text Solution
|
- Which one the following compounds has very poor leaving froup?
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following is least reactive compound for nulceophili...
Text Solution
|
- A tertiary alcohol (H) upon acid-catalysed dehydration gives a product...
Text Solution
|
- A tertiary alcohol H upon acid- catalyzed dehydration gives a product ...
Text Solution
|
- A tertiary alcohol H upon acid- catalyzed dehydration gives a product ...
Text Solution
|
- The compound P is :
Text Solution
|
- The compound Q is :
Text Solution
|
- The compound R is :
Text Solution
|
- Observe the following reaction : Ar-C-Hoverset(OH^(-))hArr[X]overset(...
Text Solution
|
- Observe the following reaction : Ar-C-Hoverset(OH^(-))hArr[X]overset(...
Text Solution
|
- Observe the following reaction : Ar-C-Hoverset(OH^(-))hArr[X]overset(...
Text Solution
|
- P+Qoverset(Aq.K(2)CO(3))underset(Delta)toRoverset(HCN)toSoverset(H(3)O...
Text Solution
|
- P+Qoverset(Aq.K(2)CO(3))underset(Delta)toRoverset(HCN)toSoverset(H(3)O...
Text Solution
|
- P+Qoverset(Aq.K(2)CO(3))underset(Delta)toRoverset(HCN)toSoverset(H(3)O...
Text Solution
|
- The structure of alkene (P) is
Text Solution
|
- The structure of product ( R ) is
Text Solution
|
- match the following
Text Solution
|