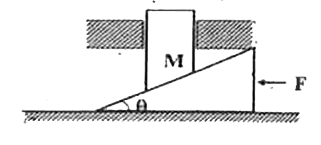
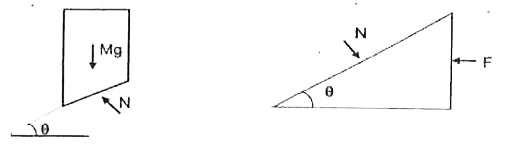
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
FIITJEE|Exercise SOLVED PROBLEMS ( OBJECTIVE)|18 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
FIITJEE|Exercise SOLVED PROBLEMS ( OBJECTIVE) ASSERTION REASONING TYPE|1 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
FIITJEE|Exercise COMPREHENSIONS ( Comprehension-II)|5 VideosTEST PAPERS
FIITJEE|Exercise PHYSICS|747 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-WORK, ENERGY AND POWER -SOLVED PROBLEMS (SUBJECTIVE )
- In the figure shown one end of a light spring of natural length l(0)=s...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth wedges of equal mass m are placed as shown in figure. All s...
Text Solution
|
- What is the power required to push the woodn wedge horizontally with c...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected by a spring of stiffn...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m moving with a velocity v(0) on a rough horizontal su...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is attached to the celling of a cabin with an in...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal plane supports a plank with a bar of mass m=1.0kg placed ...
Text Solution
|
- A small block is projected with a speed v( 0) on a horizontal track pl...
Text Solution
|