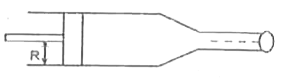
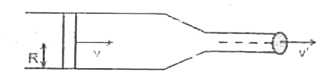
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
FLUID MECHANICS
FIITJEE|Exercise LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE|2 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
FIITJEE|Exercise LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE I|1 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
FIITJEE|Exercise SOLVED PROBLEMS (SUBJECTIVE)|10 VideosELECTROSTATICS
FIITJEE|Exercise Example|14 VideosGENERAL PHYSICS
FIITJEE|Exercise MATRIX MATCH TYPE|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-FLUID MECHANICS -SOLVED PROBLEMS (OBJECTIVE )
- A cube of mass m and density D is suspended from a point P by a spring...
Text Solution
|
- An ice cube containing a galss ball is floating on the surface of wate...
Text Solution
|
- A piston of a syringe pushes a liquid with a speed of 1 c, / sec ...
Text Solution
|
- A light cylindrical vessel is kept on a horizontal surface it's base a...
Text Solution
|
- Water rises to a height of 10 cm in a capillary tube and mercury falls...
Text Solution
|
- Excess pressure inside one soap bubble is four times that of other. Th...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a model of perfume atomizer . When the bulb A is ...
Text Solution
|
- An air bubble of diameter 2mm rises steadily through a solution of den...
Text Solution
|
- The density of ice is xgm//c c and that of water is y gm//c c. What is...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of metal weights 210 grams in air 180 grams n water and 120 g...
Text Solution
|
- When an air bubble moves up from the bottom of a lake
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a cylindrical vessel of height 90 cm filled upto the brim...
Text Solution
|
- When a drop splits up into number of drops
Text Solution
|
- A vertical capillary tube with inside radius 0.25 mm is submerged ...
Text Solution
|