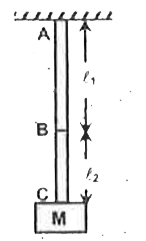
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELASTICITY AND WAVES
FIITJEE|Exercise Assignment Problems (Objective) Level-I|40 VideosELASTICITY AND WAVES
FIITJEE|Exercise Assignment Problems (Objective) Level-II|15 VideosELASTICITY AND WAVES
FIITJEE|Exercise Assignment Problems (Subjective) Level-I (Fill in the blanks )|5 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
FIITJEE|Exercise Comprehension -4|3 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
FIITJEE|Exercise EXERCISE|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-ELASTICITY AND WAVES -Assignment Problems (Subjective) Level-II & III
- A steel wire fixed at both ends has a fundamental frequency of 200 Hz....
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length L is fixed at both ends such that F is tension in it....
Text Solution
|
- The speed of sound in hydrogen is 1270 ms^(-1) at temperature T. the s...
Text Solution
|
- Two point sources of sound are kept at a separation of 10 cm. They vib...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform string is clamped at x=0 and x = L and is vibrating in its f...
Text Solution
|
- The air column in a pipe closed at one end is made to vibrate in its s...
Text Solution
|
- A copper rod of length l=50 cm is clamped at its midpoint. Find the nu...
Text Solution
|
- A loop of rope is whirled at a high angular velocityomega, so that it ...
Text Solution
|
- A piston is fitted in a cylindrical tube of small cross section with t...
Text Solution
|
- Three tuning forks with unknown frequencies f1,f2 and f3 are vibrated....
Text Solution
|
- Two rods AB and BC of equal cross-sectional area A and Young's constan...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary wave is given by y = 5 sin (pi x)/( 3) cos 40 pi t whe...
Text Solution
|
- A long wire PQR is made by joining two wires PQ and QR of equal radii....
Text Solution
|
- The first obertone of an open organ pipe beats with the first overtone...
Text Solution
|
- A boat is travelling in a river with a speed 10 m//s along the stream ...
Text Solution
|