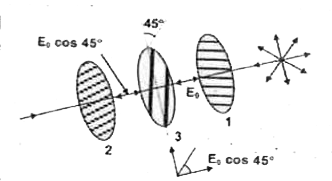
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE & WAVE OPTICS
FIITJEE|Exercise SOLVED PROBLEMS Objective: Level-I|10 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE & WAVE OPTICS
FIITJEE|Exercise SOLVED PROBLEMS Objective: Level-II|10 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE & WAVE OPTICS
FIITJEE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS Objective : Level-II (MULTI CHOICE SINGLE CORRECT)|21 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND AC CURRENT
FIITJEE|Exercise Example|15 VideosELECTROSTANTICS
FIITJEE|Exercise MATRIX MATCH TYPE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE & WAVE OPTICS-SOLVED PROBLEMS (subjective )
- Light waves can be polarised but sound waves cannot be. Why?
Text Solution
|
- Certain sunglasses use a polarizing material to reduce the intensity o...
Text Solution
|
- What minimal value can the Brewester angle have when light falls from ...
Text Solution
|
- When light is incident on a transparent dielectric at the Brewester an...
Text Solution
|
- Two poalroids are placed at 90^(@) to eachother and the transmitted in...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a graph that shows the dependence of intensity of transmitted lig...
Text Solution
|
- A person uses + 1.5 D glasses to have normal vision from 25 cm onwards...
Text Solution
|
- An astronomical telescope has a magnifying power of 10. In normal adju...
Text Solution
|
- The objective of telescope A has a diameter 3 times that of the object...
Text Solution
|
- Define magnifying power and resolving power of a telescope.
Text Solution
|
- Why is diffraction of sound waves easier to observe than diffraction o...
Text Solution
|
- Radiowaves diffract pronouncedly around buildings, while light waves, ...
Text Solution
|
- Do you think that interference pattern in Young's double slit experime...
Text Solution
|
- The distance between the first and fifth minima of a single slit diffr...
Text Solution
|
- A single slit is illuminated by light of wavelength lambda(1) and lamb...
Text Solution
|
- Find the intensities of the first three secondary maxima in the single...
Text Solution
|
- Light of wavelength 5 xx 10^(-7)m is diffracted by an aperture of widt...
Text Solution
|
- Parallel light of wavelength 5000 Å falls normally on a single slit. T...
Text Solution
|
- Monochromatic. light falls on a single slit having a width of 6.0xx10^...
Text Solution
|
- Two narrow slits are illuminated by a single monochromatic source. Nam...
Text Solution
|