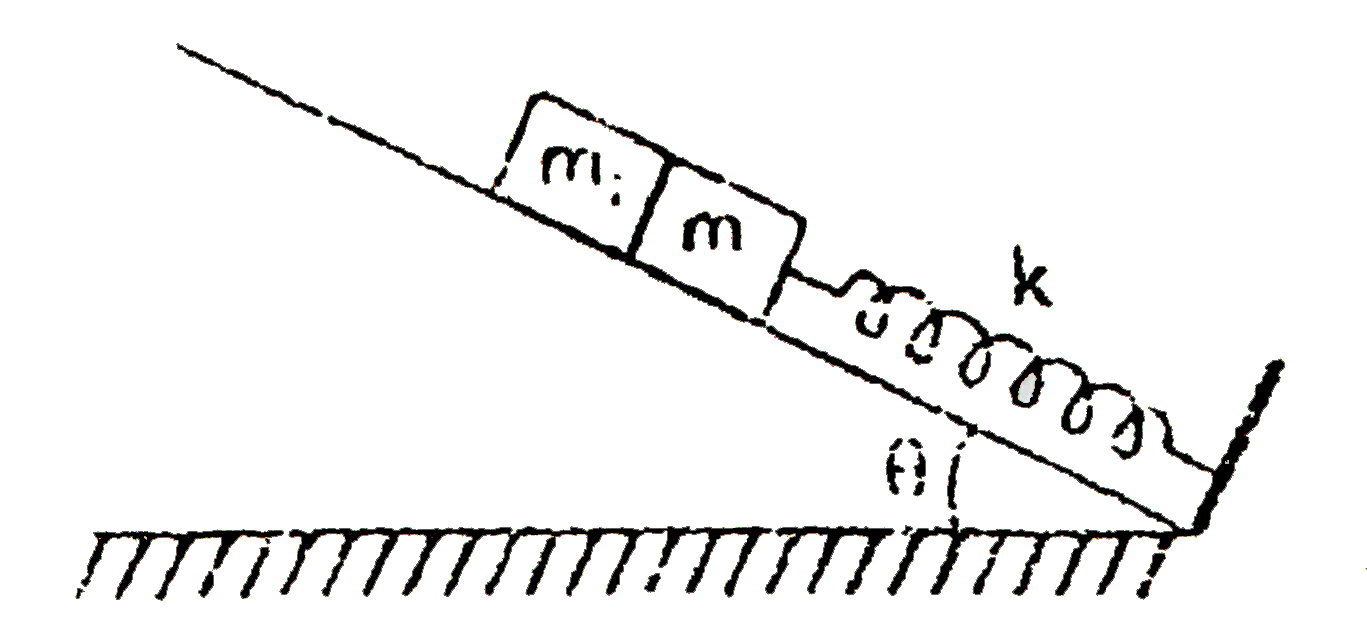
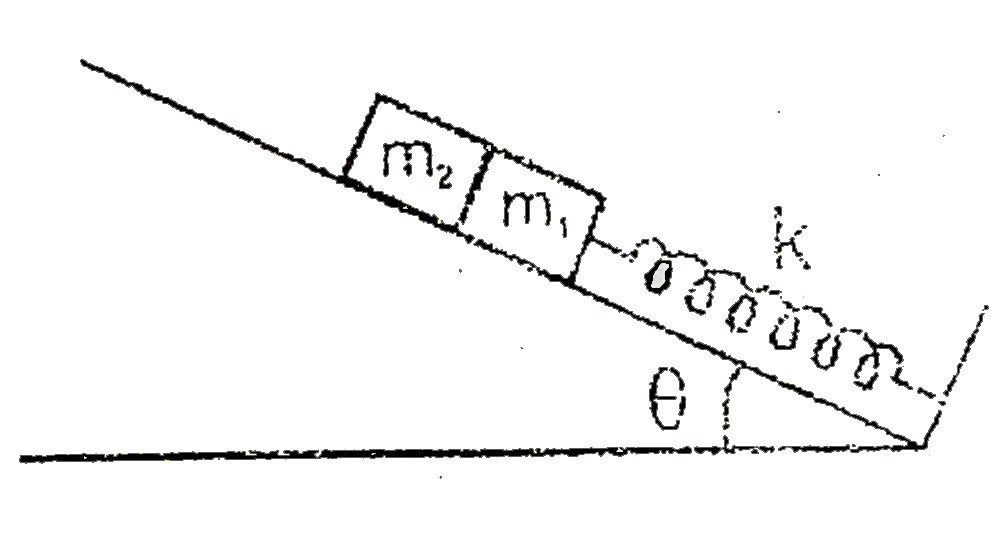
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise- 3, PART - I|20 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise- 3, PART - II|17 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise- 2, PART - III|12 VideosSEMICONDUCTORS
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise 3|88 VideosTEST PAPERS
RESONANCE|Exercise FST-3|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION -Exercise- 2, PART - IV
- A 2kg block hangs without vibrating at the bottom end of a spring with...
Text Solution
|
- A 2kg block hangs without vibrating at the bottom end of a spring with...
Text Solution
|
- Passage X) A 2kg block hangs without vibrating at the bottom end of a ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 'm' moves on a horizont smooth line AB of length 'a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 'm' moves on a horizont smooth line AB of length 'a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 'm' moves on a horizont smooth line AB of length 'a...
Text Solution
|
- Spring of spring constant k is attached with a block of mass m(1), as ...
Text Solution
|
- Spring of spring constant k is attached with a block of mass m(1), as ...
Text Solution
|