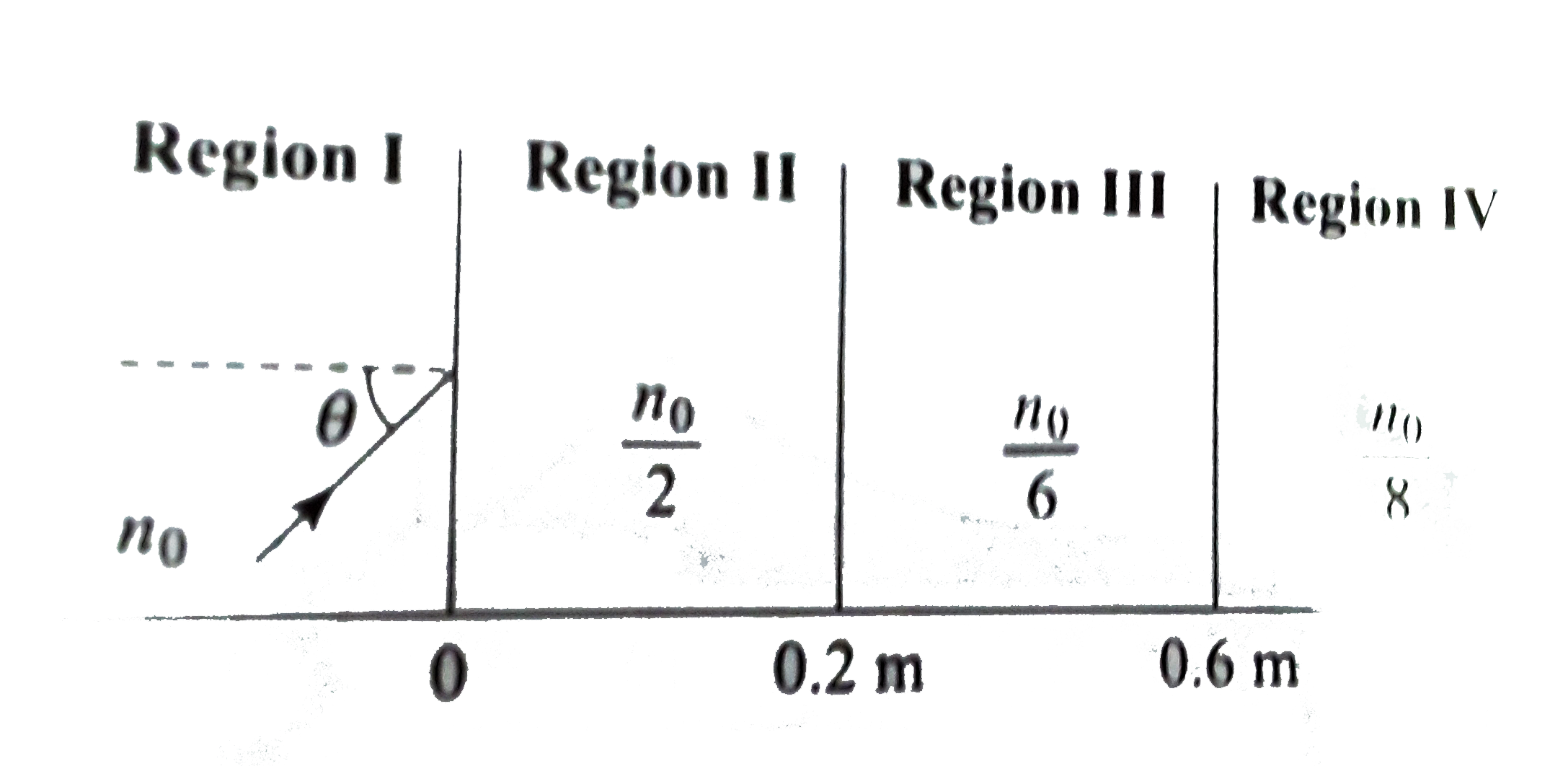A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-GEOMATRICAL OPTICS -Exercise-3
- STATEMENT-1 The formula connecting u,v and f for a spherical mirrors w...
Text Solution
|
- Two beams of red and violet colours are made to pass separately throug...
Text Solution
|
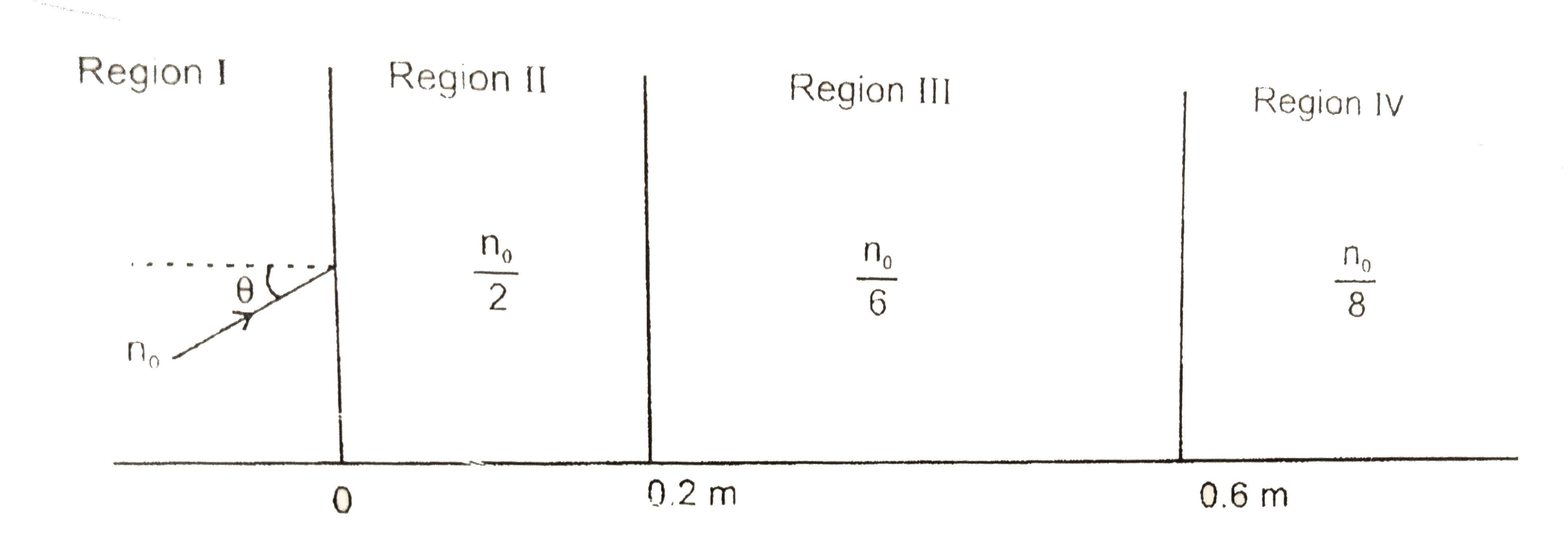
- A light beam is traveling from Region I to region IV (refer figure). T...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped from a height of 20 m above the surface of water in ...
Text Solution
|
- A student performed the experiment of determination of focal length of...
Text Solution
|
- A ray OP of monochromatic light is incident on the face AB of prism AB...
Text Solution
|
- The focal length of a thin biconvex lens is 20 cm. When an object is m...
Text Solution
|
- A biconvex lens of focal length 15 cm is in front of a plane mirror. T...
Text Solution
|
- Image of an object approaching a convex mirror of radius of curvature ...
Text Solution
|
- A large glass slabe (mu=5//3) of thickness 8cm is placed over a point ...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray travelling in glass medium is incident of glass- air inter...
Text Solution
|
- Water (with refractive index = 4/3) in a tank is 18 cm deep. Oil of re...
Text Solution
|
- A bi-convex lens is formed with two thin plano-convex lenses as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- Most materials have the refractive index, n gt 1. So, when a light ray...
Text Solution
|
- Most materials have the refractive index, n gt 1. So, when a light ray...
Text Solution
|
- The image of an object, formed by a plano-convex lens at a distance of...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in the direction (1)/(2)(hati,+sqrt3hatj) is...
Text Solution
|
- A transparent thin film of uniform thickness and refractive index n(1)...
Text Solution
|
- A point source S is placed at the bottom of a transparent block of hei...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a concave mirror and a convex lens (refractive index 1.5) of ...
Text Solution
|