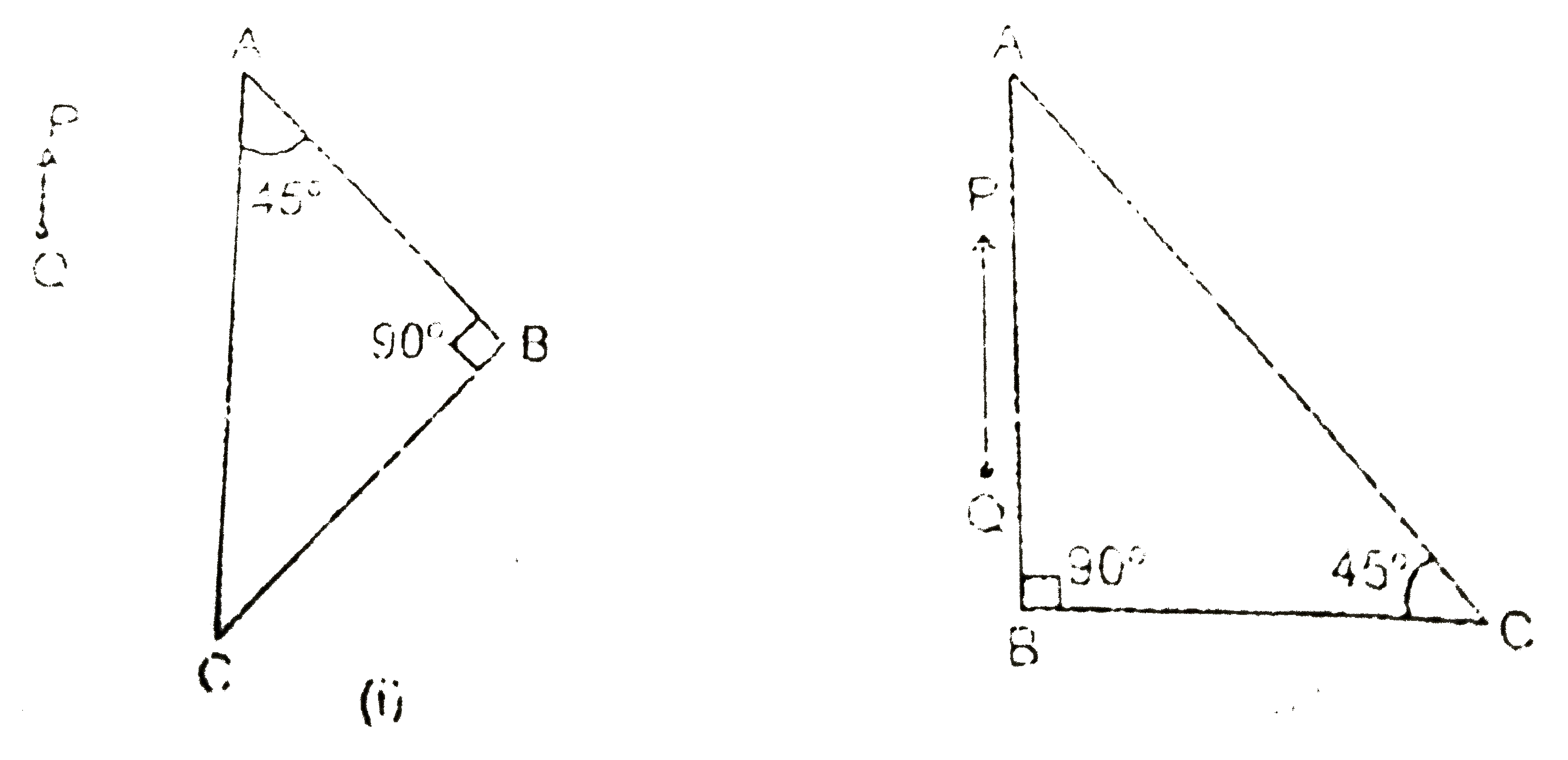
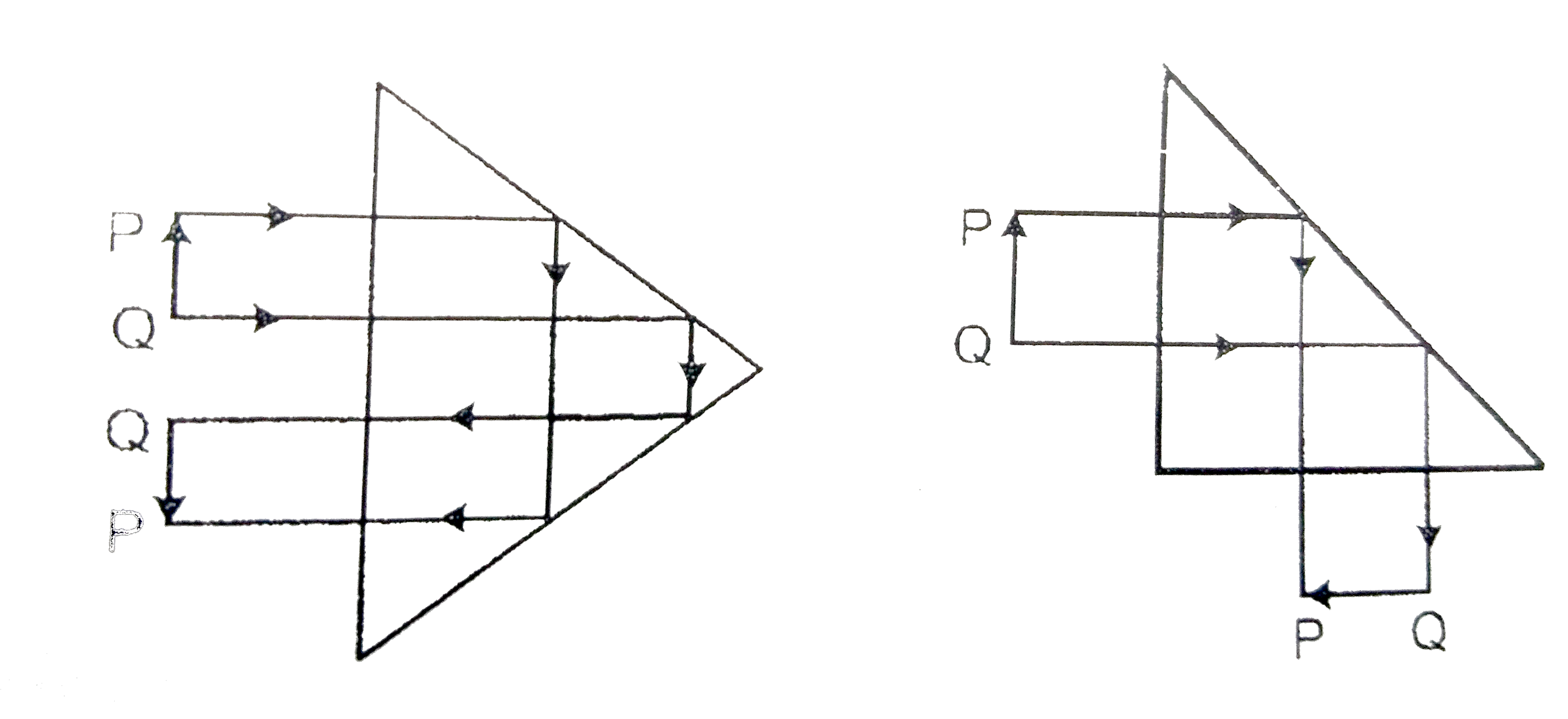
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-GEOMATRICAL OPTICS -Exercise-3
- A green light is incident from the water to the air - water interface ...
Text Solution
|
- Monochromatic light is incident on a glass prism of angle A. If the re...
Text Solution
|
- A right-angle crown glass prism with critical angle 41^(@) is placed b...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light falls on a mirror normally. What are the values of angl...
Text Solution
|
- What is far-sightedness or hypermatropia? What cause hypermetropia How...
Text Solution
|
- A double convex lens of glass of refractive index 1.6 has its both sur...
Text Solution
|
- A convex mirror always produces a virtual image of real object indepen...
Text Solution
|
- A converging lens of refractive index 1.5 is kept in a liquid medium h...
Text Solution
|
- What is the main reason for axial charomatic aberration in the formati...
Text Solution
|
- An equiconvex lens, with redii of curvature of magnitude 10 cm each, i...
Text Solution
|
- What is the ratio of velocities of two light waves travelling in vacuu...
Text Solution
|
- (a) For a ray of light travelling from a denser medium of refractive ...
Text Solution
|
- Derive the lens formula, (1)/(f)=(1)/(v)-(1)/(u) for a concave lens, u...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light passing through an equilateral traingular glass prism f...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Draw a ray diagram showing the passage of light through a glass pr...
Text Solution
|
- A glass lens of refractive index 1.5 is placed in a trough of liquid....
Text Solution
|
- Why are convex mirrors used as side view mirrors in cars ?
Text Solution
|
- Three light rays red (R), green (G) and blue (B) are incident on a rig...
Text Solution
|
- The for point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is...
Text Solution
|
- (a) (i) Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image in ...
Text Solution
|