Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRAUMENTS -EXERCISE- 4 One or more than one correct answer type
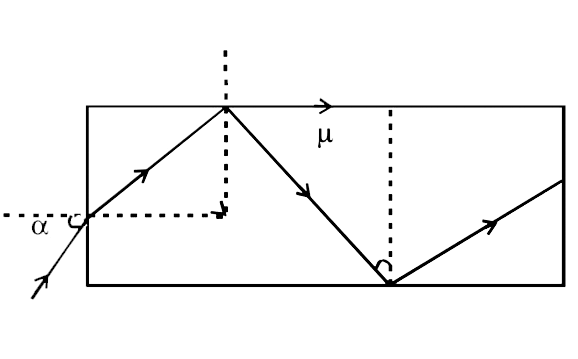
- Light is incident at an angle alpha on one planar end of a transparent...
Text Solution
|
- Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane thr...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular block of glass ABCD has a refractive index 1.6. A pin is...
Text Solution
|
- Between the primary and secondary rainbows, there is a dark band known...
Text Solution
|
- A magnifying glass is used, as the object to be viewed can be brought ...
Text Solution
|
- An astronomical refractive telescope has an objective of focal length ...
Text Solution
|
- The box of a pin hole camera, of length L, has a hole of radius a . It...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment for determination of refractive index of glass of a p...
Text Solution
|
- An object 2.4 m in front of a lens forms a sharp image on a film 12 cm...
Text Solution
|
- The graph between angle of deviation (delta) and angle of incidence (i...
Text Solution
|
- The diameter of a plano convex lens is 6 cm and thickness at the centr...
Text Solution
|
- A thin convex lens made from crown glass (mu = 3//2) has focal length ...
Text Solution
|
- A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at...
Text Solution
|
- Monochromatic light is incident on a glass prism ABC of angle A. If th...
Text Solution
|