Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-OSCILLATIONS-ILLUSTRATION
- The system of simple pendulum is immersed in liquid of a density rho(l...
Text Solution
|
- Find the time period in each of the following cases, if the mass is pu...
Text Solution
|
- The system is pulled to an elongation A and Then released. Find the mi...
Text Solution
|
- A 50 gm mass at the end of a spring vibrates in SHM. The amplitude of ...
Text Solution
|
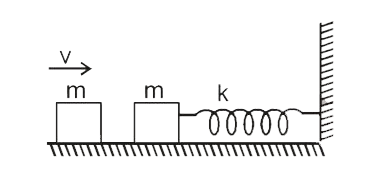
- The left block in figure collides inelastically with the right block a...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a spring of force constant k is fixed to a vertical wall an...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal platform vibrate up and down with a simple harmonic motio...
Text Solution
|
- Find time period of oscillation of the system.
Text Solution
|
- The surface shown in the diagram are smooth and all collisions are ela...
Text Solution
|
- Total mechanical energy of an oscillator is 160 J. Its force constant ...
Text Solution
|
- A point particle of mass 0.1kg is executing SHM of amplitude 0.1m. Whe...
Text Solution
|
- The average energy in one time period in simple harmonic motion is
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves on the X-axis according to the equation x = x(0) sin^...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is dropped in a tunnel dug along the diameter of ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass 'm' is suspended at a point R/2 above its centre. Find ...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum oscillates simple harmonically. The tension in the s...
Text Solution
|
- The end of the rod which is connected to the spring is pushed down and...
Text Solution
|
- In a damped oscillation amplitude at (t = 0) is A(0) and at (t = T) it...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of a damped oscillator of mass 1kg is (d^(2)y)/(dt^(2)) =...
Text Solution
|
- D is disturbed, and ultimately all the pendulums start oscillating. Ma...
Text Solution
|